P Bhoopathi, N Lee, A Pradhan, X Shen, S Das, D Sarkar, L Emdad, P Fisher (2016)
mda-7/IL-24 Induces Cell Death in Neuroblastoma
through a Novel Mechanism Involving AIF and ATM
Cancer Research, June 2016 76:12
mda-7/IL-24 Induces Cell Death in Neuroblastoma
through a Novel Mechanism Involving AIF and ATM
Cancer Research, June 2016 76:12
(Translated by Krishna Karamsetty)
Support: FACS Analysis
|
FACS analysis otherwise known as flow cytometry is a way of detecting the physical characteristics of a group of cells or particles in a lysate. For flow cytometry, the cells are exposed to a fluorescent dye that covers the cut DNA strands and are run through a machine called a flow cytometer. In the machine, the cells go through a narrow tube in a singular formation where a laser detects the fluorescent dye. As the cells are passing through the channel and the light is being illuminated, a series of sensors detects the types of lights that are refracted or emitted from the cells. The flow cytometry machine gives the number of cells that are tagged with the fluorescent dye. In the case of this article, the more cells that are counted, the cells are in the process of dying due to the infection of the virus and the introduction of MDA-7.
|
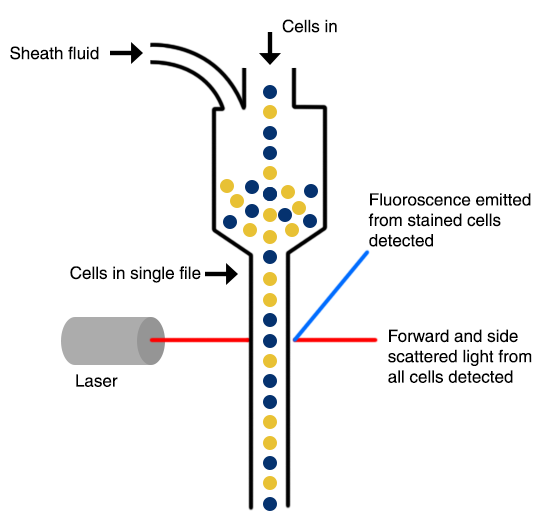
|
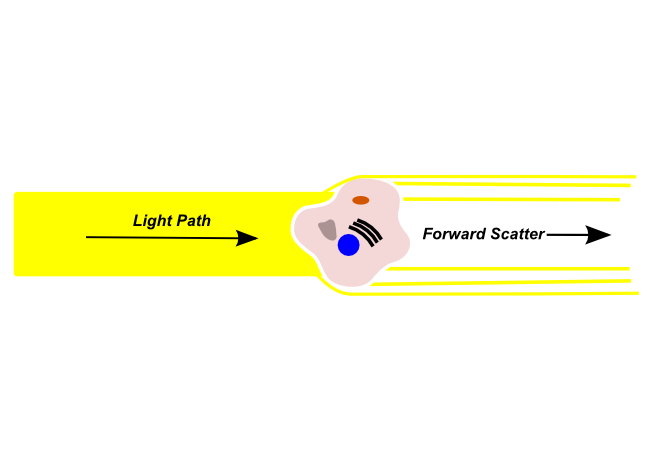
Foward scattered light is refracted by a cell in the channel and continues along the light path. These lights are typically used to determine the size of the cell.
|
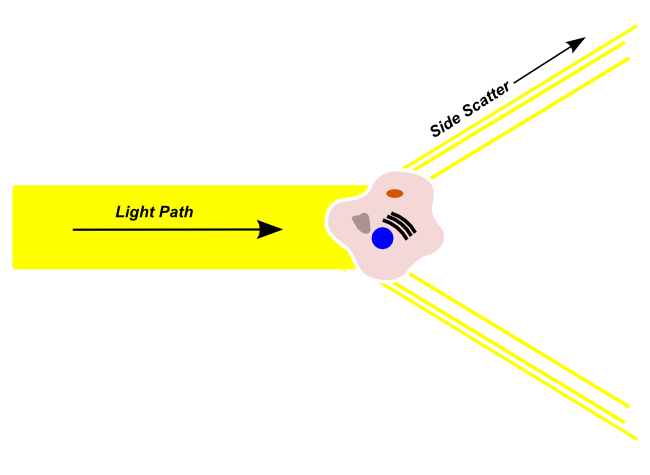
Side scattered light is refracted by a cell in the channel and deviates from the original light path. The lights are picked up by sensors diagonal to the channel. These lights are typically used to determine the complexity of the cell.
|
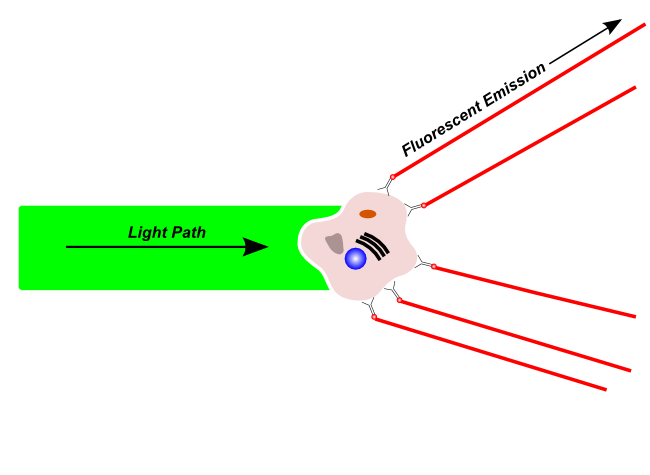
Fluoresence emission is light that is given off by the cell after it is excited by a compatible laser. This fluoresence can emit from natural materials within the cell or dyes or tagged antibodies on the cell itself.
|
References
- Robinson, Ryan, and Stefan Pellenz. “Ryan Robinson and Stefan Pellenz.” ELISA Kits - Antibodies - Research Products, 6 Dec. 2013, www.antibodies-online.com/resources/17/1247/what-is-flow-cytometry-facs-analysis/..