P Bhoopathi, N Lee, A Pradhan, X Shen, S Das, D Sarkar, L Emdad, P Fisher (2016)
mda-7/IL-24 Induces Cell Death in Neuroblastoma
through a Novel Mechanism Involving AIF and ATM
Cancer Research, June 2016 76:12
mda-7/IL-24 Induces Cell Death in Neuroblastoma
through a Novel Mechanism Involving AIF and ATM
Cancer Research, June 2016 76:12
(Translated by Krishna Karamsetty)
Introduction
|
Neuroblastoma is the most frequent solid tumorAn abnormal mass of cells. Can either be harmless or harmful found outside the brain in children under five years old. This form of cancer affects about 1 in 7,000 children and it has been speculated that it forms because of a rapid growth of neuroblasts during fetal growth. A neuroblast is a kind of embryonic cellRelating to the growth of an embryo or a baby in development from which nerve fibers which later bundle together to form the axons of a neuron.
| |
|
|
|
|
When neuroblastoma is detected in young infants younger than 5 years, it often presents itself as a heterogenousDiverse in the kind of cells that are growing mass both clinically and biologically[1]. When neuroblastoma is diagnosed however, most doctors assume that the tumor has metastasized. There are four stages of neuroblastoma. In stage I and II, the cancer is confined to the original location however as soon as it enters stages III and IV, the cancer will travel to other locations [1].
|
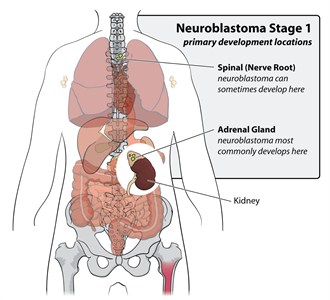
|
|
Once the cancer has entered stage III and IV, it expands persistently even when being treated with numerous rigorous therapies [1][2]. The presentation of tumors in advanced stages along with the lack of surgery options leads to a very poor patient prognosisLikely course of a disease.
|
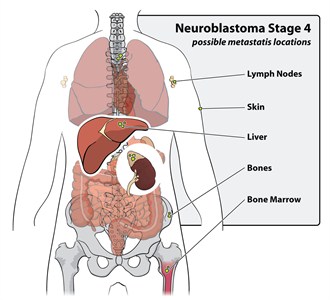
|
|
However there have been some successes in treating neuroblastoma with numerous kinds of therapies combined, but the there is a major problem with these therapies. Since neuroblastoma affects very young children, these rigorous therapies will raise the toxicity levels in the body and most of the time, after a course in chemotherapy, the neuroblastoma will return. This relapse means that these therapy options don’t work in the long run.
| |
|
|
|
|
MDA-7/Il-24 is a unique gene that shows wide antitumor activity in many different kinds of cancer without harming normal healthy cells or tissues. When MDA-7 is expressed forcibly, it promotes direct cancer killing through the production of proteins necessary to cause programmed cell death. MDA-7 also shows these antitumor properties in vitroExperiments done in petri dishes and in vivoExperiments done in live subjects which has allowed it to successfully enter clinical trials. To greatly increase the effectiveness of this gene, a specialized virus was created.
| |
References
- P Bhoopathi, N Lee, A Pradhan, X Shen, S Das, D Sarkar, L Emdad, P Fisher (2016) mda-7/IL-24 Induces Cell Death in Neuroblastoma through a Novel Mechanism Involving AIF and ATM, Cancer Research, June 2016 76:12
- Jiang H, Lin JJ, Su ZZ, Goldstein NI, Fisher PB. Subtraction hybridization identifies a novel melanoma differentiation associated gene, mda-7, modulated during human melanoma differentiation, growth and progression. Oncogene 1995;11:2477–86.
- Sarkar D, Su ZZ, Vozhilla N, Park ES, Gupta P, Fisher PB. Dual cancer-specific targeting strategy cures primary and distant breast carcinomas in nude mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005;102:14034–9.