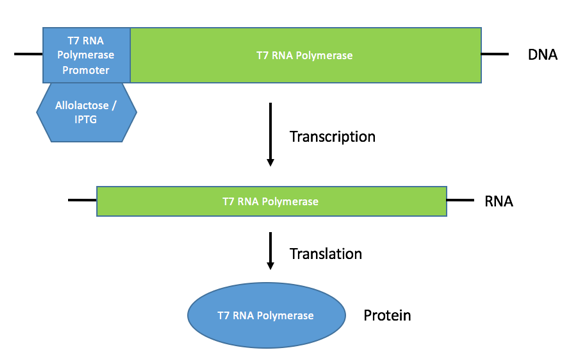
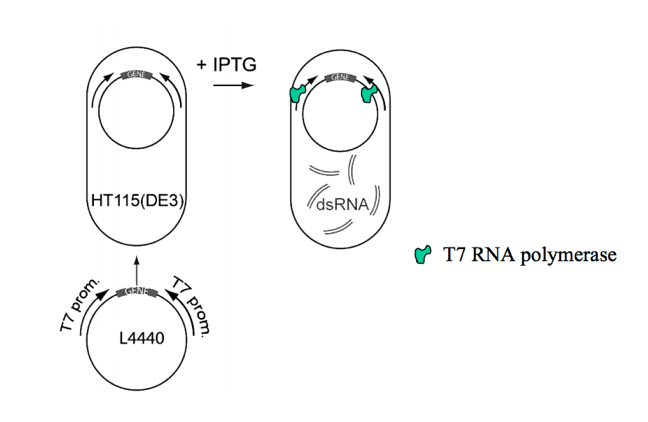
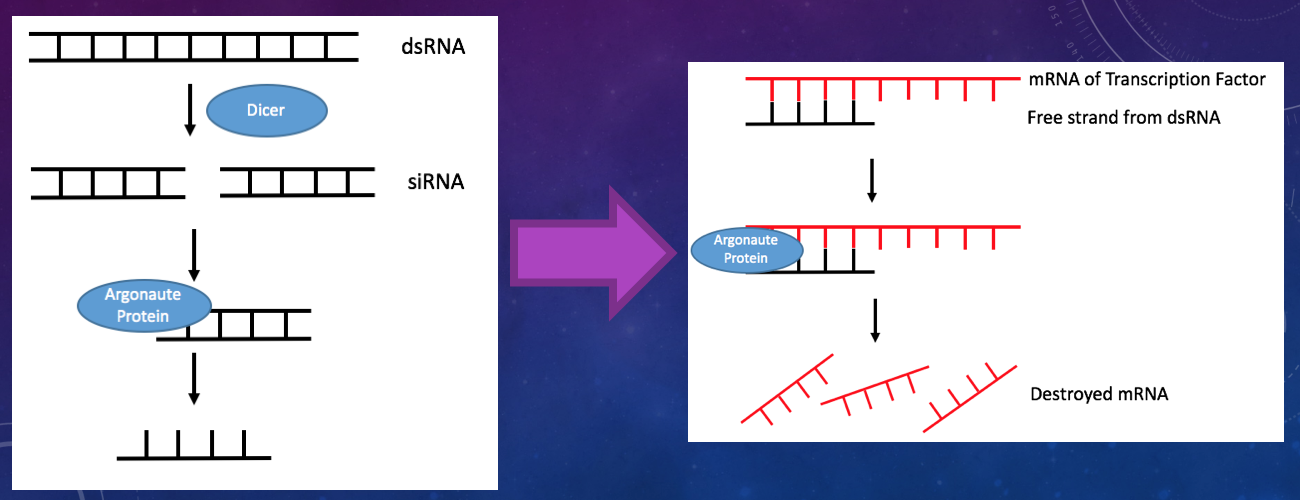
In order to knock down or inactivate each of the transcription factors, a procedure known as RNA interference (RNAi) is used. This procedure uses double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) which acts as a signal to silence the expression of specific genes in organisms when it is introduced. dsRNA acts as a signal through a pots-transcriptional mechanism, meaning it destroys the RNA that transcribes the targeted gene [1].
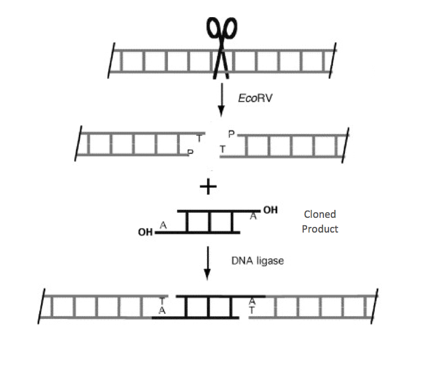
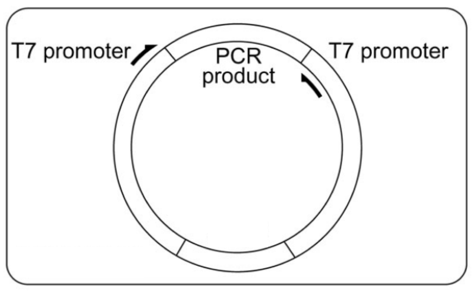
So how is dsRNA created? The first step is to identify the transcription factor of interest and its DNA sequence. Once this sequence is matched to its appropriate primer (a short DNA segment that pairs complementary to the sequence of interest), the primer can bind and DNA-polymerase will synthesize the double stranded DNA and amplify the amount of this transcription factor (a detailed explanation of how primers work can be viewed in the support page of qPCR) [2]. This PCR product can then be placed into a L4440 RNAi feeding vector. This feeding vector is what is ultimately going to help knock down the transcription factors.