When a cell is placed in conditions where it experiences a low level of oxygen, it needs to adapt accordingly. Under hypoxic conditions, the cell undergoes many rapid changes as well as slow responses. Theses slow responses have been shown to be mediated by the hypoxia inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) transcription pathway. Even though, the HIF-1 pathway has been shown to be a major factor in the cellular responses to hypoxia, there are instances where one can see transcriptional hypoxic responses that the HIF-1 pathway is unable to explain. Therefore, the question of concern is, what are the HIF-independent mediators that are critical to this hypoxic response?
Padmanabha D, Padilla PA, You Y, Baker KD (2015)
A HIF-Independent Mediator of Transcriptional Responses to Oxygen
by Deprivation in Caenorhabditis Elegans
Genetics, Vol. 199, 739-748
A HIF-Independent Mediator of Transcriptional Responses to Oxygen
by Deprivation in Caenorhabditis Elegans
Genetics, Vol. 199, 739-748
(Translated by Emaan Chaudry)
Introduction
Transcription is the process by which genes are turned "on" and "off". Transcriptional responses (the activation or suppression of the genes) are therefore important in our cells as they control when the cell undergoes transcription. Transcription factors aid in this process by binding to the promoter region of our RNA (as seen in Figure 1). When bound to the promoter region, RNA polymerase (a protein that assists in allowing transcription to occur) begins the process of transcription [1].
| 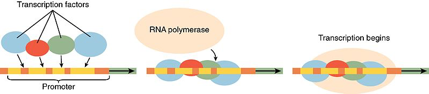
Figure 1: A basic explanation of how transcription factors work [3].
|
|
The research in this paper focuses on the regulation of a gene known as F45D3.4 which has previously been identified as a gene that is turned on independently of the HIF-1 pathway when a round worm is exposed to hypoxic conditions [2].
References
References:
1. Museum, S. (2010, April 19). Who am I? Retrieved from http://whoami.sciencemuseum.org.uk/whoami/findoutmore/yourbody/howdoyoubecomeyou/whatdoyourgenesdo 2. Shen, C., D. Nettleton, M. Jiang, S. K. Kim, and J.A. Powell-Coffman, 2005 Roles of the HIF-1 hypoxia-inducible factor during hypoxia response in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Biol. Chem. 280:20580-20588. 3. How do Transcription Factors Bind to DNA | Definition and Type of Transcription Factors, Binding Mechanism. (2017, May 24). Retrieved from http://pediaa.com/how-do-transcription-factors-bind-to-dna/ |