Under the hypoxic conditions, only 62.5% of the control animals survived, and of those, only about 75% were able to progress to adulthood. The hif-1 mutants and hif-1;blmp-1 double mutants showed no progression and were unable to survive in hypoxic conditions. The blmp-1 mutant, achieved a lower percentage in terms of developmental stage than the control, however, it was higher than the hif-1 and hif-1:blmp-1 double mutants. It can, therefore, be concluded that blmp-1 is also essential for normal development progression in hypoxic conditions. It also demonstrated that eliminating blmp-1 has negative consequences in hypoxic conditions, but they are not as detrimental as when hif-1 is eliminated completely.
Padmanabha D, Padilla PA, You Y, Baker KD (2015)
A HIF-Independent Mediator of Transcriptional Responses to Oxygen
by Deprivation in Caenorhabditis Elegans
Genetics, Vol. 199, 739-748
A HIF-Independent Mediator of Transcriptional Responses to Oxygen
by Deprivation in Caenorhabditis Elegans
Genetics, Vol. 199, 739-748
(Translated by Emaan Chaudry)
How does blmp-1 affect round worms in vivo?
Knowing that blmp-1 is what is mediating the hypoxic responsiveness of hif-independent transcripts, it is of interest to determine what the effect of eliminating blmp-1 would be on the round worms in vivo. There are consequences to not being able to respond to hypoxia. One of these consequences is a lack of development. Therefore, in this experiment, the embryos of the control animals (labeled as wt), hif-1 mutants, blmp-1 mutants, and hif-1;blmp-1 double mutants, were developed in either normoxia or hypoxia conditions. Under normoxia conditions, the control and hif-1 mutants developed equally well. However, the blmp-1 mutant and hif-1;blmp-1 double mutants achieved a slightly lower developmental stage (refer to figure 4 in the paper).
| 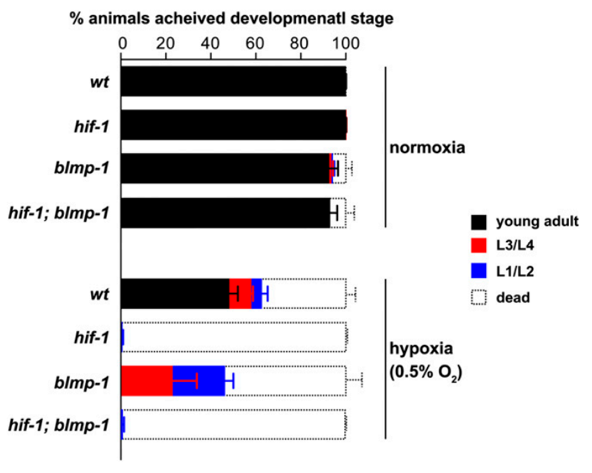
Figure 4: This is taken directly from Padmenhaba et al (2015). The image displays the effect of normoxia versus hypoxia on the developmental stages the round worms were able to reach, L1/L2 being the first stage measured, L3/L4 being the second, and young adult being the last stage.
|