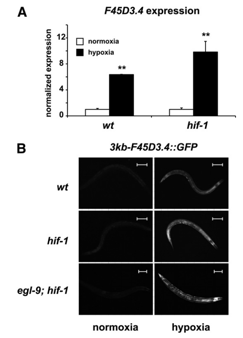
This first experiment was completed in order to determine how the F45D3.4 gene is expressed in normoxia versus hypoxia. Further, the experiment looked at whether or not it is induced when there is a HIF-1 mutant (a round worm with an inactive HIF-1 complex). This is displayed in figure 1A of the paper (as seen below), where we see that the difference in the expression of F45D3.4 under normoxia and hypoxia conditions is significantly different in both the wild type (a normal round worm) and HIF-1 mutant. These results were obtained using a method known as qPCR (more information about this method is described in the qPCR support page).
After the qPCR method was used to obtain the results displayed in figure 1A, microscopy was used to determine that the gene was only active during hypoxic conditions (explanation of how the gene was looked at under the microscope can be found in support pages). Figure 1B demonstrates that in the wild type, hif-1 mutant, and egl-9;hif-1 double mutant (a round worm with an inactive HIF-1 complex and egl-9 complex) that the F45D3.4::GFP gene is only expressed in hypoxic conditions. Egl-9 is the gene that transcribes for prolyl hydroxylase. Prolyl hydroxylase is what activates the HIF-1 pathway in normoxia. Therefore, Egl-9 is the HIF-1 pathways' "partner". The double mutant was therefore looked at to completely confirm that the F45D3.4 gene was transcribed in hypoxic conditions without any part of the HIF-1 pathway being active.