Yeast 2 Hybrid Approach: Technique used to find protein to protein interactions and protein to DNA interactions
- Process: Isolate two proteins that we want to understand whether they interact or not. Then attach two halves of a transcription activation factor, proteins that turn transcription on or off by binding to nearby gene coding regions, to both proteins. If the proteins interact then the full transcription activation factor complex will be formed and can then bind to the promoter region, region of DNA that initiates transcription of a gene, in a yeast cell and produce a measured response that will show whether the proteins interacted or not.
- Video if doesn’t make sense: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lxrbYJE8hNM
- Possibly make my own page for just explaining the figure and how it works in general
- We use a yeast cell because it is the genetically most known eukaryote
Gal4-based Y2H system
- Gal-4 is the transcriptional activator in this system
https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Outline-of-the-yeast-two-hybrid-Y2H-GAL4-system-a-The-basic-concept-of-this_fig1_51459381
Wuchty et al. (2017)
The Protein Interactome of Streptococcus pneumoniae and
Bacterial Meta-interactomes Improve Function Predictions.
mSystems 2:1-10
The Protein Interactome of Streptococcus pneumoniae and
Bacterial Meta-interactomes Improve Function Predictions.
mSystems 2:1-10
(Translated by Karun Rajesh)
Support: Yeast-2-Hybrid Approach
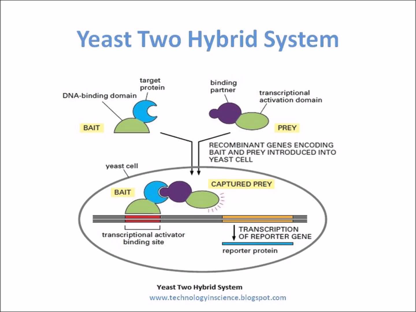
Fig. 7: Yeast-2-Hybrid System Illustrating a yeast-2-hybrid system. Two proteins are being isolated, where one is attached to a DNA-binding domain and the other is attached transcriptional activation domain. These are then brought together and if the two proteins interact, a transcriptional activator is formed, which allows for the transcription of a measured gene. If this measured gene response is seen, then it is know that the two proteins interact.
|