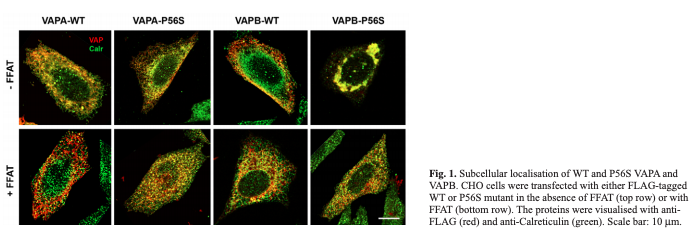
The motivation behind this experiment was to understand and visualize how VAPs behave normally under conditions of over expression of VAPA's and VAPB's respective wild types and P56S mutations. In addition to its normal behavior the desire of this experiment was to understand how VAPs behave with the presence and absence of the FFAT motif. Using Immunofluorescence allows for visual capture of diffusion of transmembrane proteins, proteins bound by the membrane, throughout the ER and Golgi apparatus in relation to the cell.
Procedure
In order to visualize this diffusion, Calreticulin and VAP-flag proteins were used as they both are "colocalized" in the cell when there is transport of transmembrane proteins from the ER to the Golgi.
The steps for Immunofluorescence:
- This is done as there aren't specific anti-bodies for fluorescence of every protein and/or it is more expensive to do so
1. Paraformaldehyde is used to fix the cells allowing cross-linkage of primary amines and stop all movement of proteins in cells
2. The cells are then permeabilized through use of the detergent Saponin, which punches holes in the cell to allow for entrance of anti-bodies
3. Junk Proteins (Goat serum + albumin) is used to block other cells from binding to fluorescence anti-bodies
4. Flag anti-bodies are attached to the beginning of the proteins of interest (VAPA/VAPB and Calreticulin)
5. Junk proteins are used again for additional binding
6. Secondary antibodies are binded to primary anti-bodies in order to enhance imaging and different colorways
7. Confocal Microscope is used for imaging
Results
VAPA WT -FFAT/+FFAT
- VAPA normally diffuses through the ER and Golgi allowing calreticulin and VAPA to move throughout the membrane
- In +FFAT calreticulin and VAPA are more spread out but have both left the ER
- VAPA normally diffuses through the ER and Golgi allowing calreticulin and VAPA to move throughout the membrane
VAPB WT -FFAT/+FFAT
- VAPB normally diffuses through the ER and Golgi allowing calreticulin and VAPB to move throughout the membrane
- Some aggregation but not significant
VAPB P56S -FFAT
- Aggregates are formed within the ER
- VAPB is trapped in the ER
- Normal diffusion of VAPB does not happen
- Immobile obstacles in the ER membrane are present not allowing newly synthesized proteins to easily leave through ER exit sites
VAPB P56S +FFAT
- VAPB normally diffuses through the ER and Golgi allowing calreticulin and VAPB to move throughout the membrane
- Some aggregation but not significant
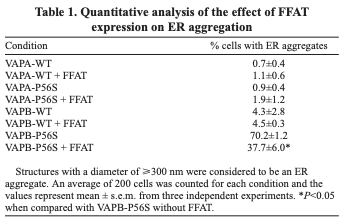
- Transmembrane proteins can't diffuse properly with expression of certain VAPs
Addition of FFAT helps in diffusion of VAPB P56S