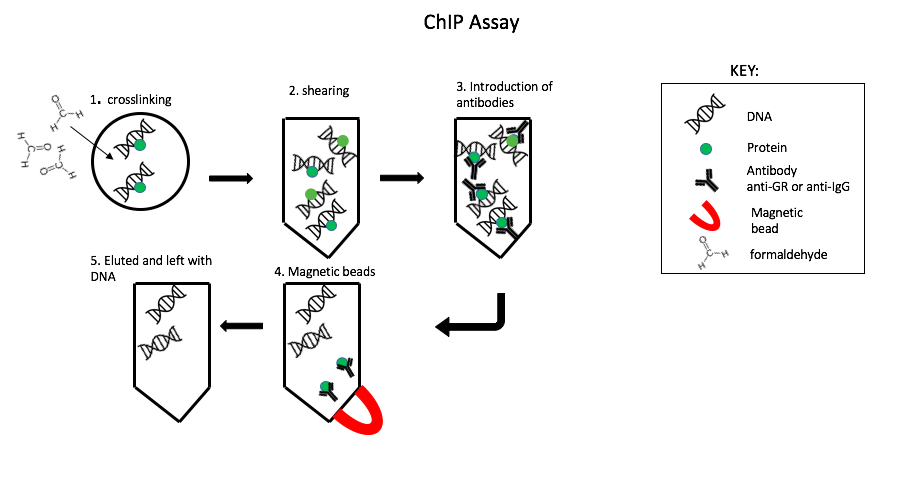
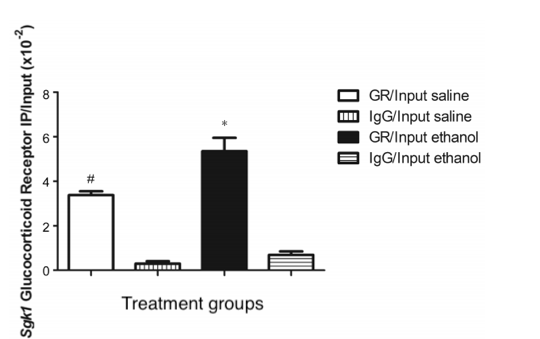
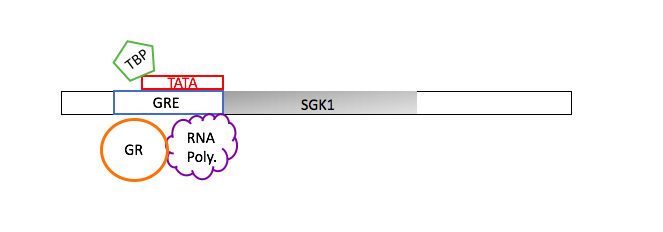
To understand the regulation of transcription a chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIp) assay was performed (Fig. 1). First, A bond formed between glucocorticoid receptor (GR) and particular DNA sequence using formaldehyde, known as cross linking. The excess DNA strands were cut up through shearing it enzymatically. Leaving behind the crosslinked DNA in small fragments and free chromatin fragments. Antibodies are like a mouth that bind onto a specific target. Two types of antibodies were introduced into the solution anti- glucocorticoid receptor (anti-GR) and anti-immunoglobin (anti-IgG). The anti-IgG is used as control because it´s commonly involved in immune response. Magnetic beads were applied to capture only the anti-body bounded protein, the remaining solution containing chromatin was eluted. Then the DNA and protein were separated by Proteinase K (reverse crosslinks)("ChIp IT", 2014). The remaining DNA was used for Quantitative - polymerase chain reaction (Q– PCR.) A ChIp assays is extremely useful because it allows us to focus on a particular DNA segment (SGK1 promotor region) through the interaction of proteins with DNA. Then find out the quantity through Q-PCR.
A Q-PCR main purpose to analyze the gene expression, by amplifying the DNA. To find out when processes is complete or almost done a SYBR green dye is introduced. This process is started by separating the two DNA strands into a single strand a process known as denaturation. The SYBR green binds to the single strands emits a low fluoresces color. Then primers (Forward- ACCCCTGCTCCCTCTAACTC and Reverse-GCGGAAATAAGTCTCTGCTCT) are introduced to allowing replication to occur. At the end of DNA replication, the two strands are of DNA are binded tightly, producing a bright florescence color. The brightness increases as the number of sets increase. Once PCR is completed the data is analyzed on a standard cure. In a quantitative measure the value around the exponential phase is taken and compared with the others.