It’s known corticosterone is produced from the adrenal gland and then flows into the bloodstream to various parts in the body and pre frontal cortex. In order to regulate physical and emotional stress by breaking down sugars into usable energy.
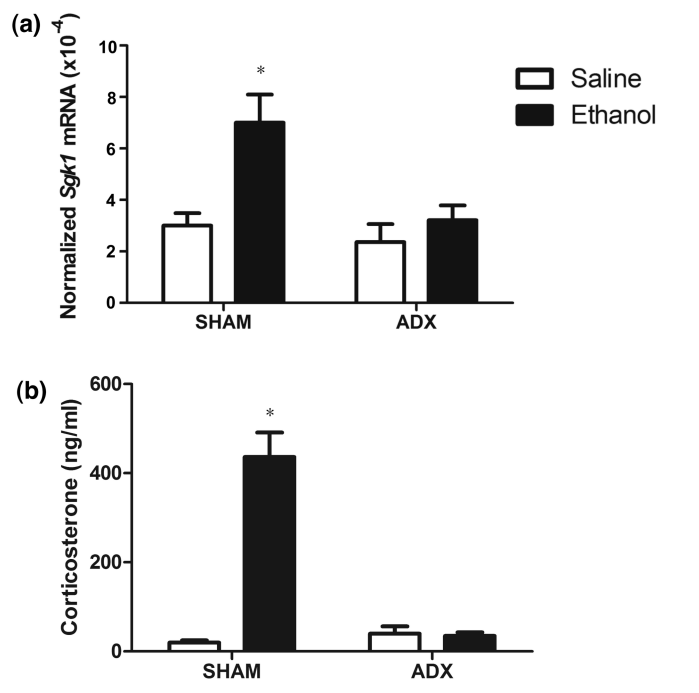
The mice were split into two treatment groups called SHAM and (adrenalectomy) ADX. The ADX mice had gone through a surgery removing the adrenal glands. The SHAM group represents mice who had gone through a placebo surgery, putting them through the stress of a normal surgery but with normal conditions (no adrenal gland removed.) This allowed them to test if corticosterone levels are affected by other regions in the body. Furthermore, since corticosterone levels are known to be directly correlated to expression levels of sgk1 mRNA. Each treatment group was tested for corticosterone levels and mRNA sgk1 transcription. The data was collected through a Q-rtPCR (more information can be found at this link)
According to the data SHAM mice, there was a distinct different in levels between the ethanol and saline solutions. The mice exposed to ethanol had an upregulation of sgk1. In the ADX mice there was barely any difference between ethanol and saline in the production of corticosterone or sgk1. Thus, it can be concluded that the adrenal gland is the only one responsible for the high levels of corticosterone. Overall this experiment expands the knowledge about the molecular pathway of skgk1 in the presence of alcohol. The upregulation of sgk1 is directly linked to the adrenal gland producing large amounts of corticosterone into the blood stream, increasing the transcription of sgk1.