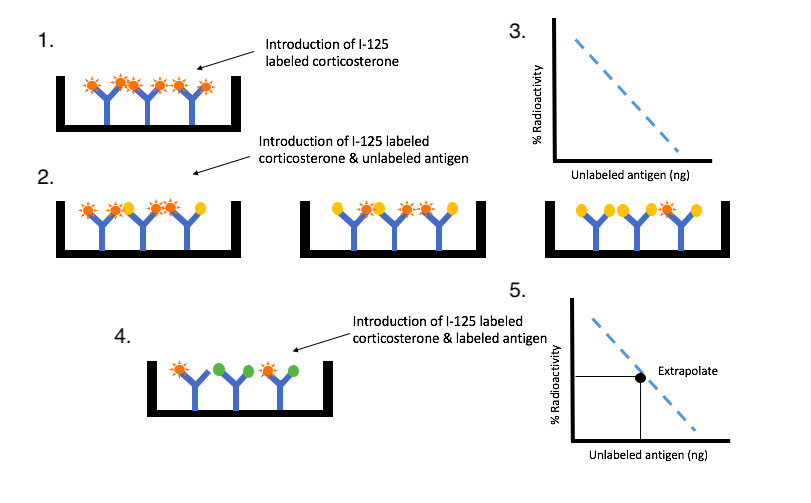
The data was collected between four treatment groups: SS, SE, EE, and ES. Support.To obtain the levels of corticosterone in the blood stream a radioimmunoassay(RIA) was performed (Fig. 1) . The purpose of a RIA to measure the concentration of an antigen, in this case corticosterone. A blood sample was taken from mice’s trunk and further separated through centrifuge. An antibody against the antigen that will bind to the corticosterone in the sample. There are two types on antigens, a radioactive I-125 antigen and unlabeled antigen(___). A microtiter plate is set up with antibodies with radioactive antigens added to the cell. The radioactive antigens will saturate the binding site of all the antibodies, resulting with 100% radioactivity (Fig. 1 part 1). Then in a second cell the same amount of radioactive antigens and increasing known concentrations of unlabeled antigens will be added to a second cell(Fig. 1 part 2). The antibodies in the cell have the same affinity for the antigens. Thus, the antigens will compete with one another for the binding site. As the proportion of unlabeled antigens increase, the radioactivity will decrease. Since the unlabeled antigen will have replaced the radioactive antigen. A standard curve will be obtained, illustrating a negative linear relationship between the percent of radioactivity to the concentration of unlabeled antigens (Fig. 1 part 3).
In order to determine the amount of antigen (corticosterone) present in the sample. The experiment will be repeated, but this time the cell will contain radioactive antigens and the antigen from the blood sample(Fig. 1 part 4). Both of these antigens will compete for the binding site. This will show the amount of radioactivity present in cell. Then the value of radioactivity will be used to extrapolate the concentration of corticosterone in the blood sample(Fig. 1 part 5)(Goldsmith, 1975.)
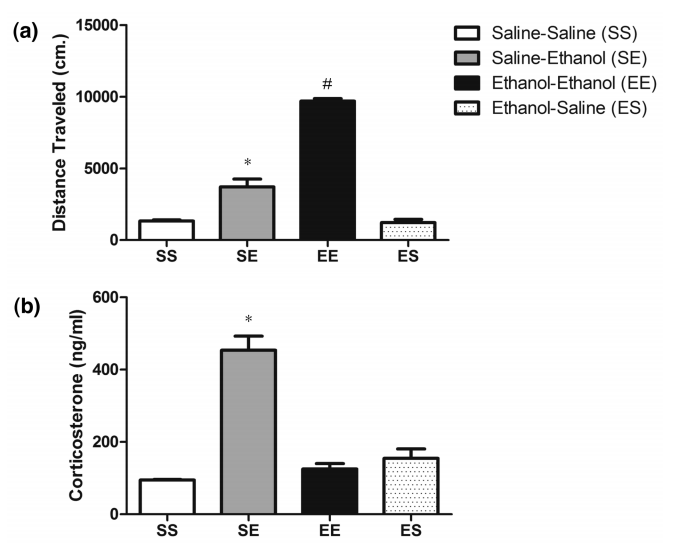
This was repeated for each of the treatment groups, giving the results shown ( Fig. 2.) The largest amount of corticosterone was present in the SE treatment group. Acute ethanol stimulated the adrenal gland to produce large amount of corticosterone in response to the stress. Thus, it can be concluded the levels of corticosterone correlate with sgk1 mRNA expression levels. On the other hand, EE levels decreased. Since mice were already exposed to saline and ethanol. The constant stimuli of ethanol and ethanol wasn’t strong enough to produce a response, known as desensitization.