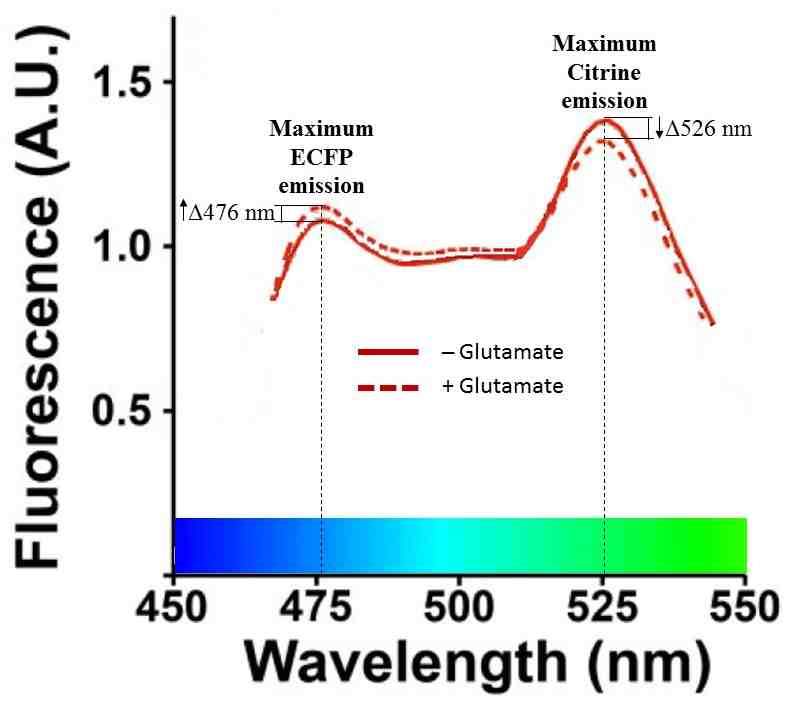
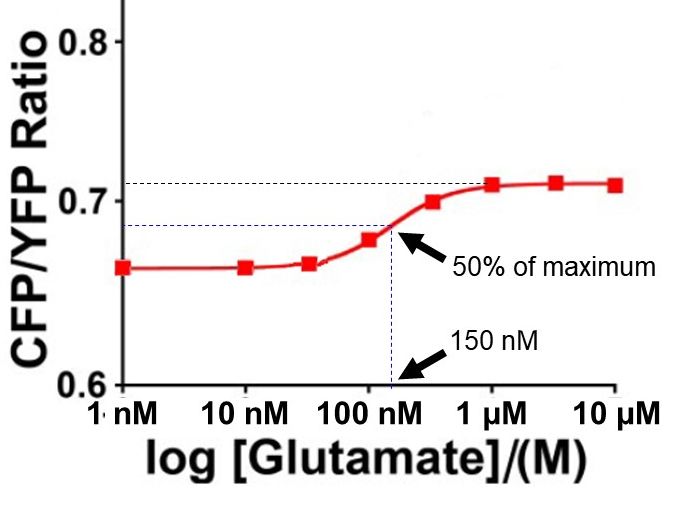
The difference can be expressed as a ratio (called CFP/YFP) of the fluorescence at 476 nm (the maximum emission of ECFPenhanced cyan fluorescent protein) to the fluorescence at 526 nm (the maximum emission of Citrinea type of yellow fluorescent protein). When glutamate is absent, this value is:
CFP/YFP [- glutamate] = 1.08/1.38 = 0.78The addition of glutamate therefore increases the CFP/YFP ratio by 0.07/0.78 = 9%. This isn't that much, but it's a start. The authors sought to increase the sensitivity of the sensor.
CFP/YFP [+ glutamate] = 1.12/1.31 = 0.85