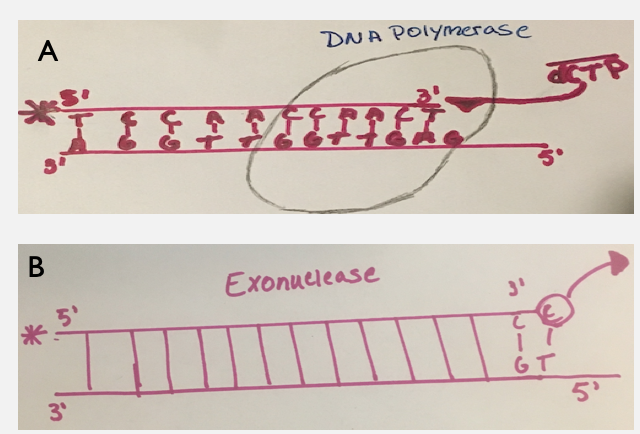
Studies in the past have been done and found that the specific enzyme that is being the most affected is, DNA polymerase gamma[5]. This specific enzyme has two functions, one synthesizes new strands of DNA (polymerase) in 5'-3' direction. The second function is the ability to proofread from the 3' to 5' direction looking for any incorrect mismatches (exonuclease) and replaces it with a correct nucleotide.[6] Past studies that have been performed say that the (-)3TC is a less toxic analog compared to its counterpart (+)3TC[7]. These studies however are not the best because when running the experiments, the researchers used such a small concentration of mitochondrial DNA polymerase that it would not exist as a holoenzyme. With the availability of constructing a pure human mitochondrial DNA polymerase this allows for a deeper and thorough analysis[9].
The main goal of the researchers is to look at the incorporation of an exonucleaseThe polymerase activity which cuts incorrect nucleotides activity, efficiency, and time it takes for the binding to occur. Also, the activity of the nucleoside analogsDrugs that inhibit viral replication is checked to see if it is cutting out the wrong incorporated nucleotide, and the rate at which it is cleaving and adding an analog. Both the enantiomers are compared back to the wild-type known as dCTP (dicytidine triphosphate). Comparing the nucleoside analogs back to the wild-type (dCTP) will help understand how the analogs are incorporating with mitochondrial DNA polymerase and how the polymerase is being inhibited. With the knowledge gained from the experiment this may help to design better antiviral drugs which inhibit the viral DNA polymerase rather than the human mitochondrial DNA polymerase.