To understand the mechanism of ZBTB7A regulation, the authors would like to know first whether ZBTB7A is regulated by KLF1 and whether this regulation is achieved by direct binding of KLF1 to the promoter of ZBTB7A gene. The focus of this summary is to explain the Chromatin Immunoprecipitation – Sequencing (ChIP-Seq) experiment that was used to show whether regulation of ZBTB7A by KLF1 is achieved by direct binding of KLF1 to the promoter of ZBTB7A gene.
Laura J. Norton, Alister P.W. Funnell (2017)
KLF1 directly activates expression of the novel fetal globin repressor ZBTB7A/LRF in erythroid cells
Blood Advances 1:685-692
KLF1 directly activates expression of the novel fetal globin repressor ZBTB7A/LRF in erythroid cells
Blood Advances 1:685-692
(Translated by Wassal Alhammad)
Abstract
|
The Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) is an invaluable method for studying interactions between specific proteins or modified forms of proteins and a genomic DNA region. It also can be used to determine whether a transcription factor interacts with a candidate target gene. In this article ChIP experiment were conducted to see whether ZBTB7A is regulated by direct binding of KLF1 to the promtor of ZBTB7A gene. The experiment was conducted on two types of cells, KLF1-inducible estrogen receptor (K1ER) erythroblast cells and human umbilical cord blood–derived erythroid progenitor-2 (HUDEP-2) cells. These two types pf cells were chosen because they can be matured to red blood cells. Using ChIP-Seq, this article showed that KLF1 binds strongly to ZBTB7A promoter in K1ER and HUDEP-2 cells. Their findings tell us that KLF1 regulate ZBTB7A by direct binding. This discovery could be translated into therapeutic modalities to reduce Sickle-cell anemia and β-thalassemia diseases by altering the expression of KLF1 which will alter the expression of ZBTB7A. |
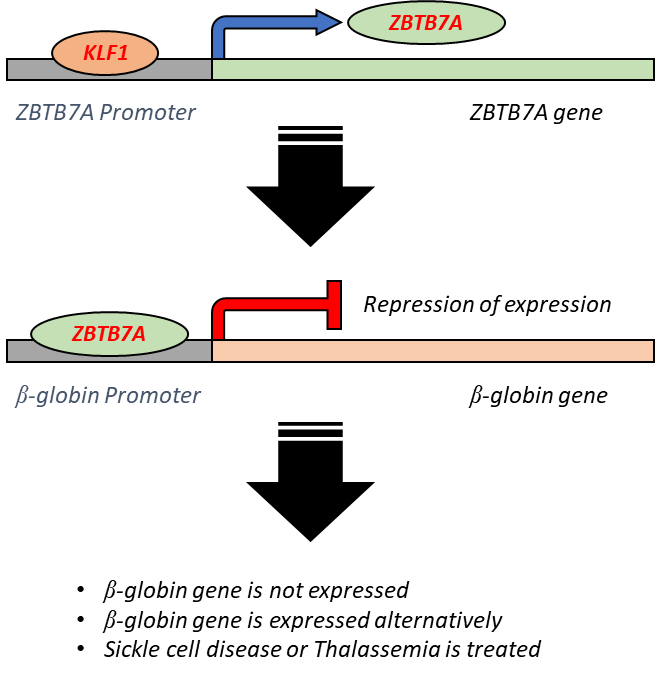
Fig. 2:The mechanism of ZBTB7A regulation by KLF1: KLF1 increase ZBTB7A expression by binding to its gene promoter (top). ZBTB7A protein pinds to peta-globin promoter and prevent peta-globin gene from expression (bottom) |
|
|