Understanding how can KLF1 regulate the expression of ZBTB7A in erythroid cells by direct binding to its promoter will help in reducing, SCD, sickle-cell diseases. The figure in the right shows a comparison of a normal red-blood and sickle-cell cells, which blocks the blood flows in the body [3].
Laura J. Norton, Alister P.W. Funnell (2017)
KLF1 directly activates expression of the novel fetal globin repressor ZBTB7A/LRF in erythroid cells
Blood Advances 1:685-692
KLF1 directly activates expression of the novel fetal globin repressor ZBTB7A/LRF in erythroid cells
Blood Advances 1:685-692
(Translated by Wassal Alhammad)
Introduction
|
Sickle-cell anemia and β-thalassemia are widespread genetic diseases that are caused by the disruption of adult β-globin genes[1]. As discovered from the Fetal Hemoglobin (HbF) analysis, reactivating this gene lead to significant amelioration of these diseases. It has been known that BCL11A represses the expression of fetal hemoglobin through direct activity of Kruppel-like transcription factor 1 (KLF1). A second layer of fetal hemoglobin repression is achieved by the activity of transcriptional factor repressor called ZBTB7A. Norton et al sought to figure out whether KLF1 regulates the ZBTB7A repression activity by direct binding to the ZBTB7A promoter.
|
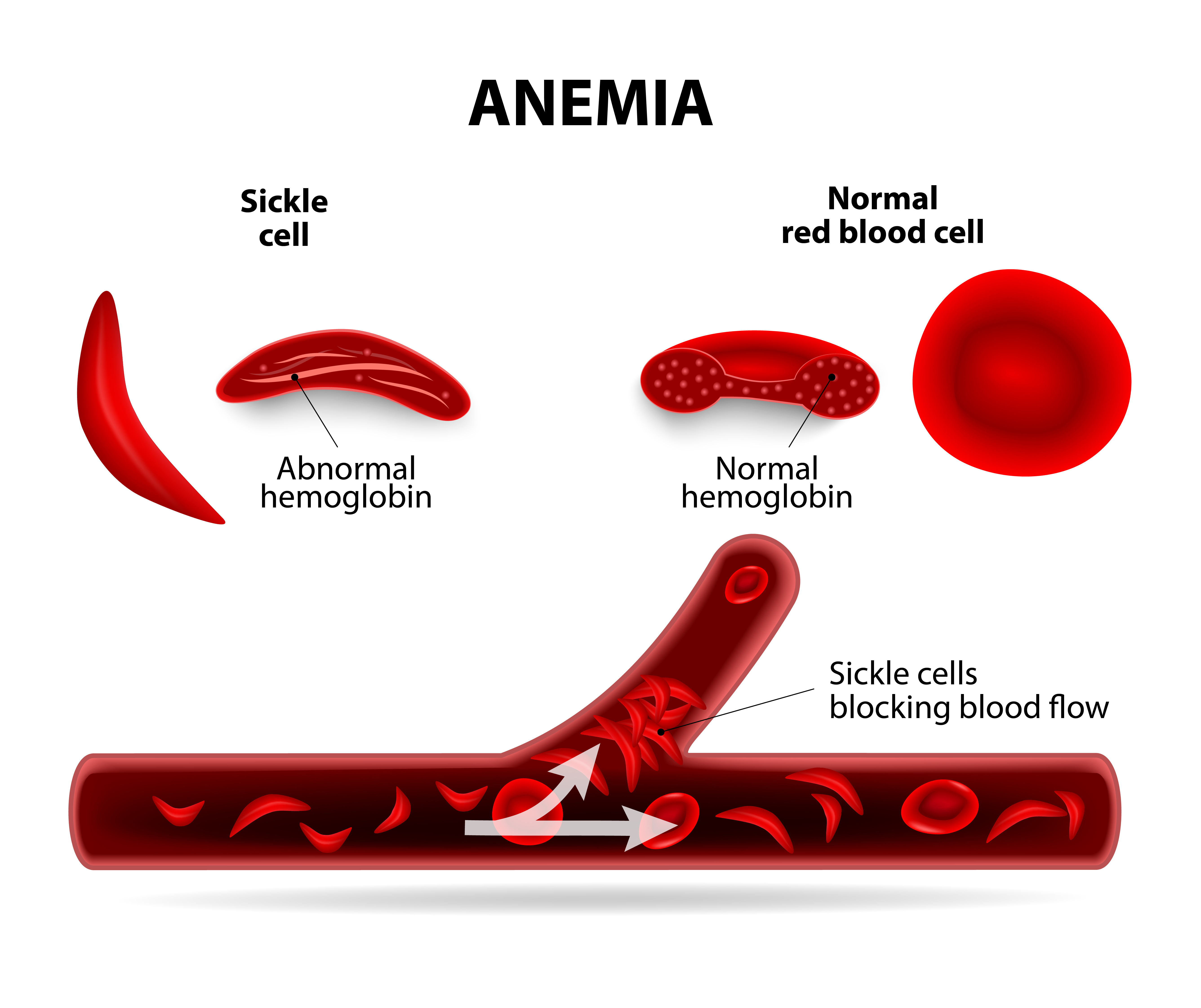
Fig. 3: comparison of a normal red-blood and sickle-cell cells: The normal cells, which has a normal hemeglobin protein, transpost oxygen from to the cells perfectly (right), but the sickle-cell, which has an abnormal hemeglobin protein, (left) block the blood flow, resulting in blood clots (bottom) .From CIRMWEB (2015). |
|
Any cells contain nucleus and inside it there are chromosomes. These chromosomes are made of DNA and various types of proteins such as histones and other DNA bound-proteins. The composite of DNA and proteins is called Chromatin. A class of DNA binding proteins is called transcription factors. These proteins may promote transcription of some genes or prevent a gene from being expressed. To find whether a protein is actually bind directly to DNA and therefore, promote or suppress gene expression, we use a ChIP-Seq experiment. ChIP-Seq is an abbreviation for Chromatin Immunoprecipitation followed by DNA sequencing [2]. The purpose of Chip-Seq experiment is to locate where in the genome a specific protein bind. In our case we aim to used ChIP-Seq to figure out where in the ZBTB7A gene does KLF1 binds. |
References
- Laura J. Norton, Alister P.W. Funnell (2017). KLF1 directly activates expression of the novel fetal globin repressor ZBTB7A/LRF in erythroid cells. Blood Advances 1:685-692.
- Schmidt D, Wilson MD, Spyrou C, Brown GD, Hadfield J, Odom DT. ChIP-seq: using high-throughput sequencing to discover protein-DNA interactions. Methods. 2009;48(3):240-248.
- One-Time, Lasting Treatment for Sickle Cell Disease May be on Horizon, According to New CIRM-Funded Study. (2015) CirmWeb.