- Radioactive materials (sources), x-ray tubes, fallout (cosmic), from the ground (radium)
- To further understand radiation we need to look at the electromagnetic spectrum, the characteristics of energy waves, quantum nature of radiation, and the relationship between mass and energy
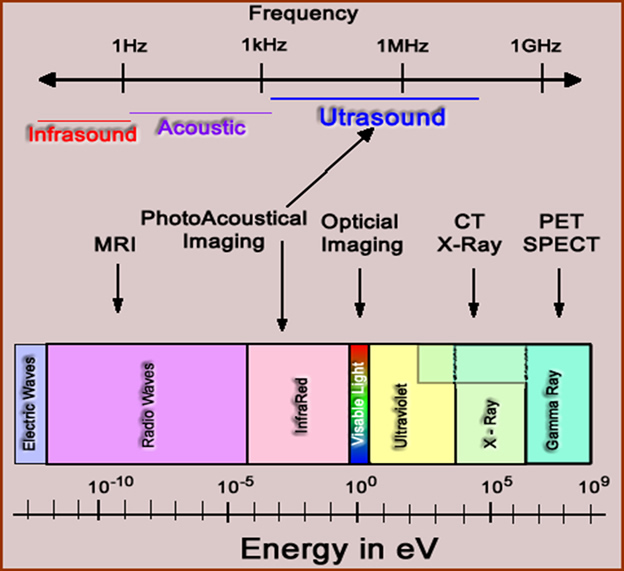
- Referred to as waves, a frequency of energy
- These frequencies are found in the electromagnetic spectrum
- Electrical frequencies has a range with the low end comprising electric/radio waves and the hight end gamma and x-rays - See the types of frequencies?
- Where is visible light?
- It is a very small part of the electromagnetic spectrum
- If you think about it, there is really very little that we can see when you consider the entire electromagnetic spectrum
- Furthermore, notices where the different imaging systems as they acquire data at different points within the spectrum
- Associated with frequency is the wave or energy wave.
- There are many types of energy waves and their frequencies vary pending where they fall on the graph above
- Most important to us are gamma rays
- Very high frequencies (such as gamma and x-ray) exhibits light and particle characteristics. This is known photons of energy. If the originate from the nucleus of an atom they we define them as gamma-rays
- The higher the frequency the more "vibrations per second" are seem within that given frequency
- Is the quantum nature of these high frequency gammas that gives gamma rays their "light and mass" properties

Return to the beginning of the document
Next Lecture - The Nature of Radiation and its Interactions
Return to the Table of Contents