Multi-Agent control design has been a topic of research for over a decade .The ideas that lead to the development of multi-agent control began around three decades ago when decentralization of control of large systems was a major topic of research. As common engineering practice, it is desirable to a have a tool that models a system in a simplistic way and yet maintain the salient features of that system. In a micro-grid, these salient features are the power and voltage distributions. Current simplified power grid simulator tools such as PowerWorld, PowerSim, Gridlab, etc, model only the power distribution features of a micro-grid while tools such as Simulink, Modelica, etc, use detailed modeling to accommodate the voltage distribution features. |
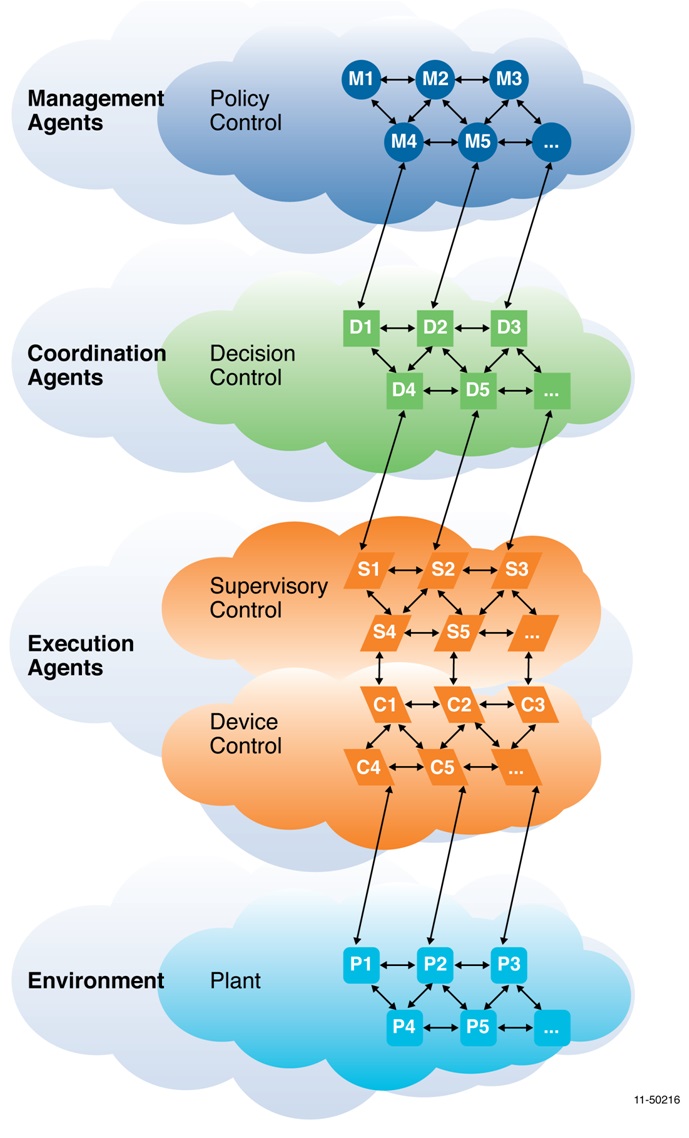
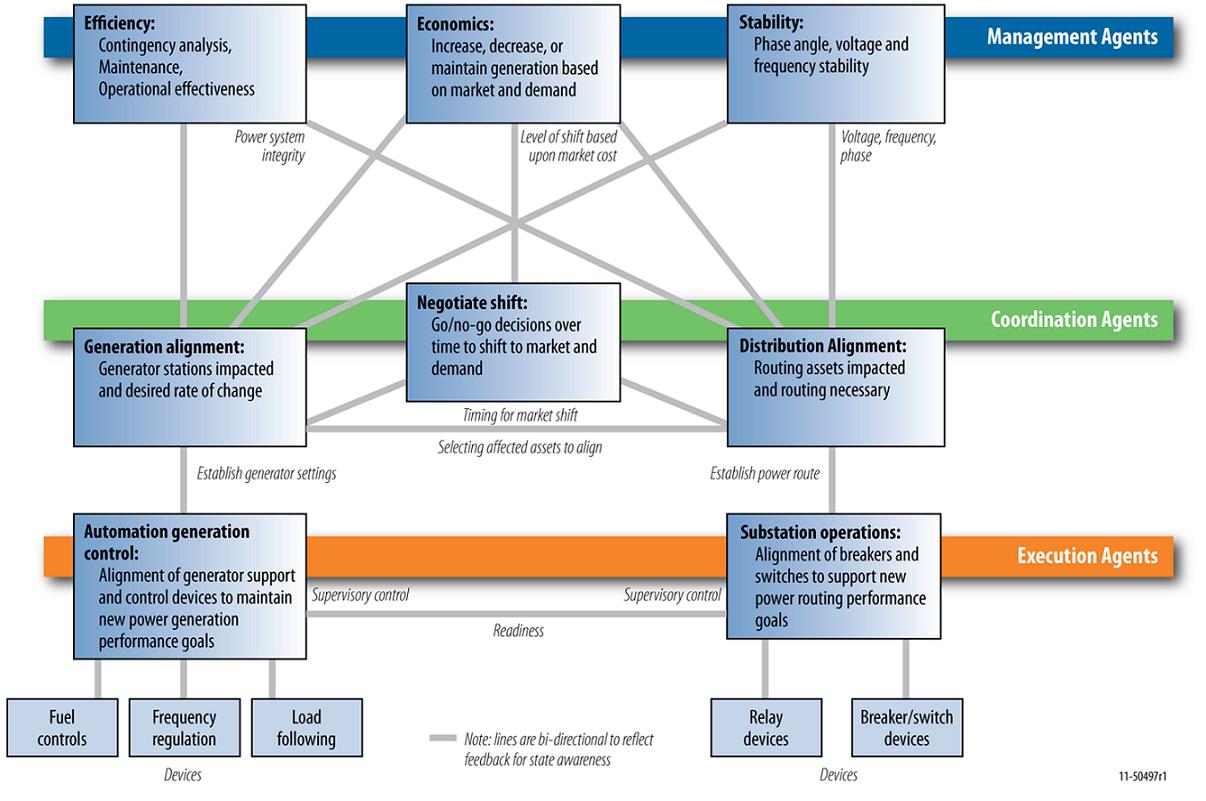
A Multi-Agent Control Scheme is a hierarchical control structure that operates the desired system in an economically efficient manner. For the Electric Power Grid, the Multi-Agent Control Scheme consists of three layers, namely the Execution Layer, the Coordination Layer and the Management Layer. Each Layer is made up of multiple agents that perform decision making and control. The Execution Layer directly monitors the sensors and controls the field devices. The Coordination layer on the other hand sets the set-points for Execution Layer that best meets the policy dictated by the Management Layer. The Management Layer sets the policy for control, i.e. the philosophical goals and priorities, against the physical constraints of the system. |


A Microgrid Simulator software is under development by our group to simulate and understand the dynamics of a microgrid. The current version of the simulator inputs point values of load and generation from the user and then runs the microgrid model to check if supply meets demand.The figure below shows an SGridSim tool. The tool consists of two user interfaces and one CAD window. The leftmost user interface consists of a main panel, an edit panel and a simulation panel while the rightmost user interface consists of a control panel and a run panel. In the leftmost panel, the main panel provides the user the means to load the desired micro-grid file for display on the CAD window. The edit panel provides the user the means to edit and save the component parameters. The simulation panel provides the user the means to run the micro-grid model. In the rightmost panel, the control panel provides the user the means to 1) set the load at the available load sectors; 2) set the desired power generation supplied by the available generators; 3) set the voltage regulating transformer impedances. The run panel provides the user feedback about status of the micro-grid in terms of the actual generation supplied to the micro-grid and the load voltage demands met based on control settings provided by the user in the control panel. The control panel is designed as such in order to enable future design work of multi-agent controllers to control the power inputs to the micro-grid and manage stability. The desired micro-grid is constructed using a configuration file that specifies the components present on the micro-grid along with their positions on the CAD window and related parameters. |

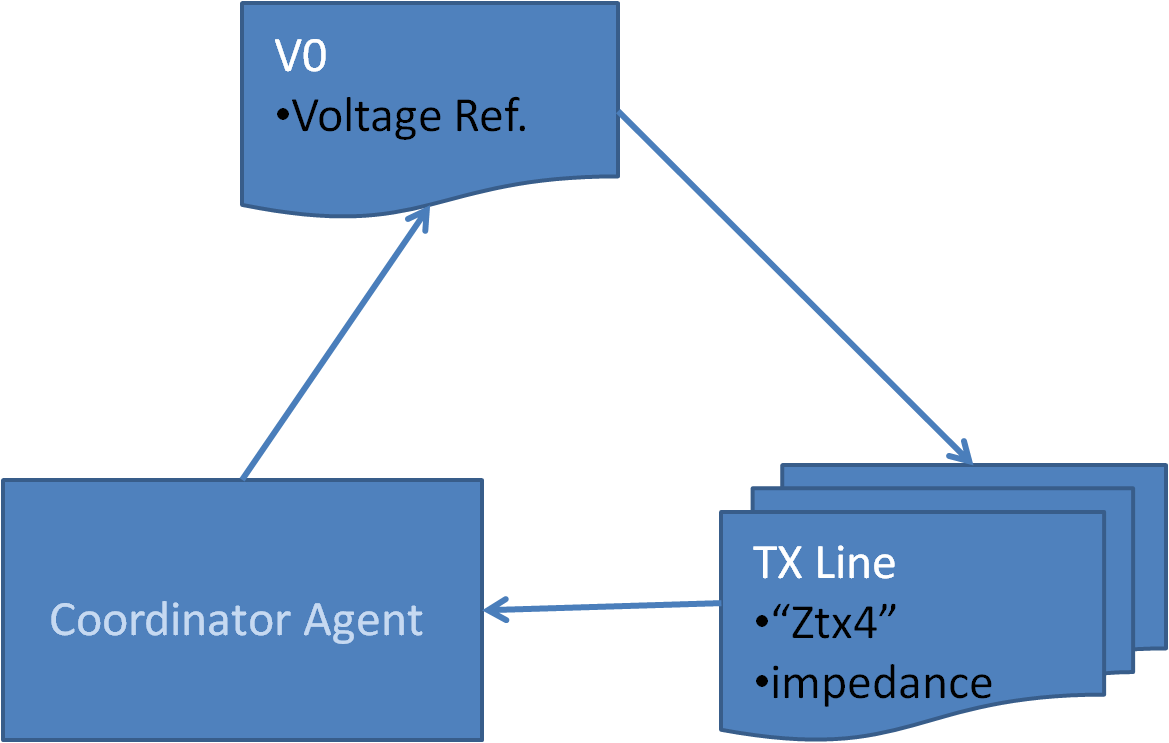
The Execution Layer is composed of Object-Oriented Agents that stores information about the components and their parameters. I also takes care of Automatic Generation Control.A Coordinator Agent sequentially calls the relevant agents to compute the required reference voltages at the generators. The Computed reference voltages are supplied to the microgrid model for simulation. |
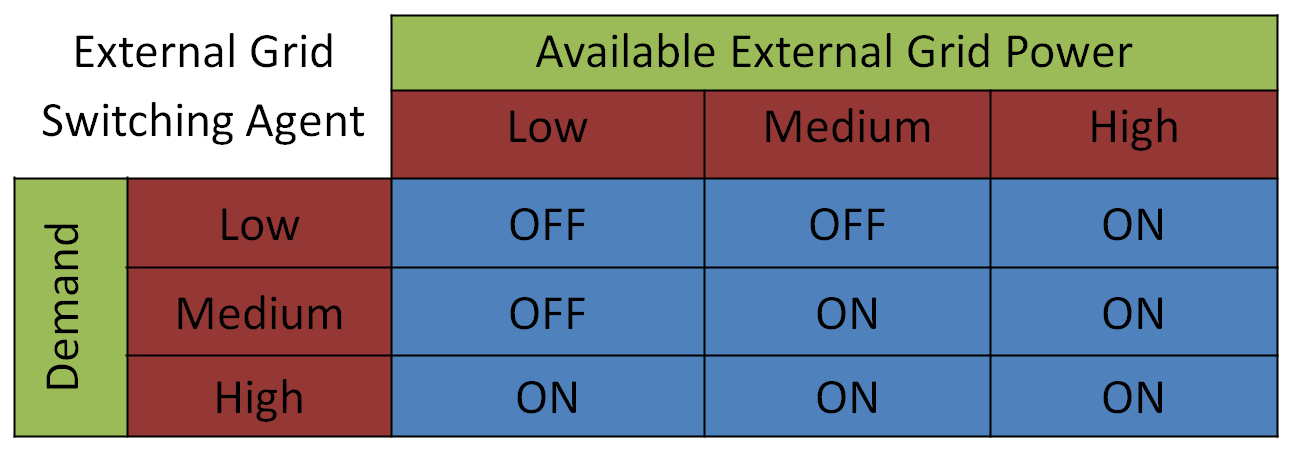
Fuzzy Logic Agents Control the switching of the wind power and external grid power to the microgrid. They also inputs total demand power and available wind and external grid powers and takes care of Substation Operation. |
 |
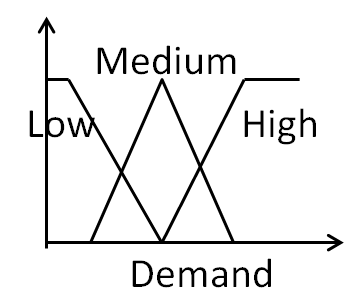 |
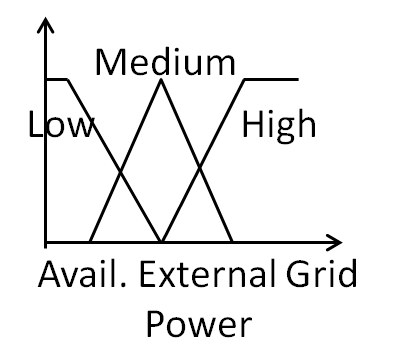 |
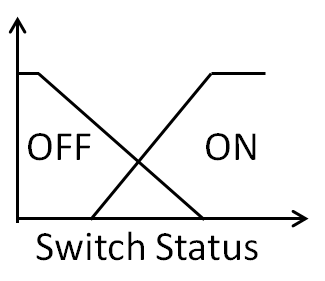 |
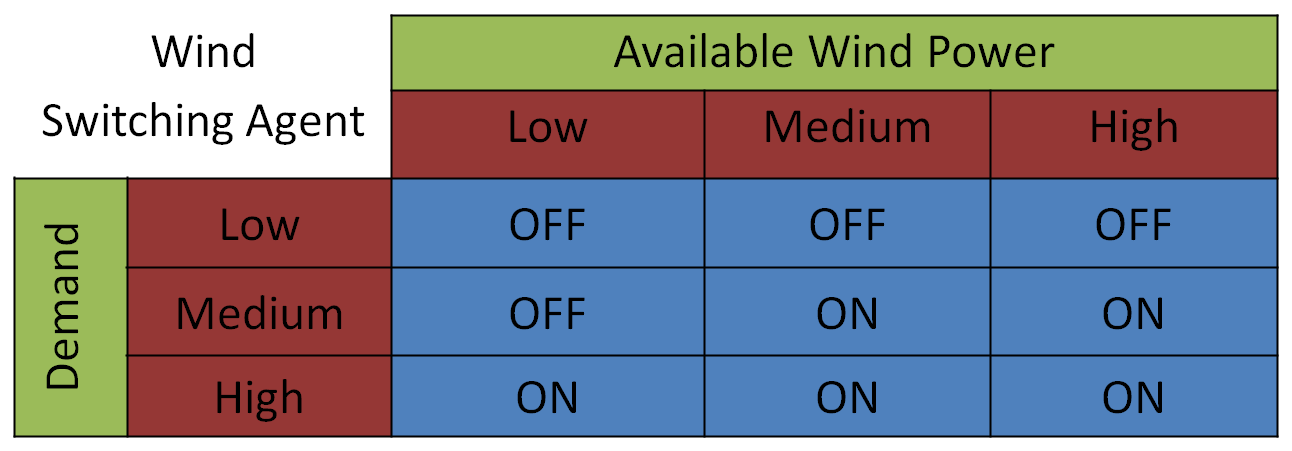 |
 |
 |
 |
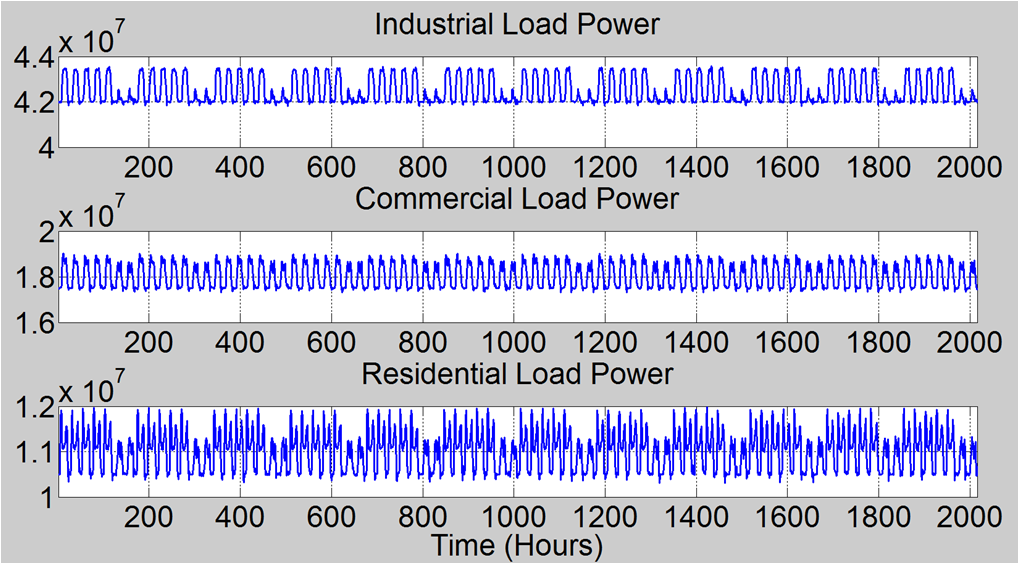 |
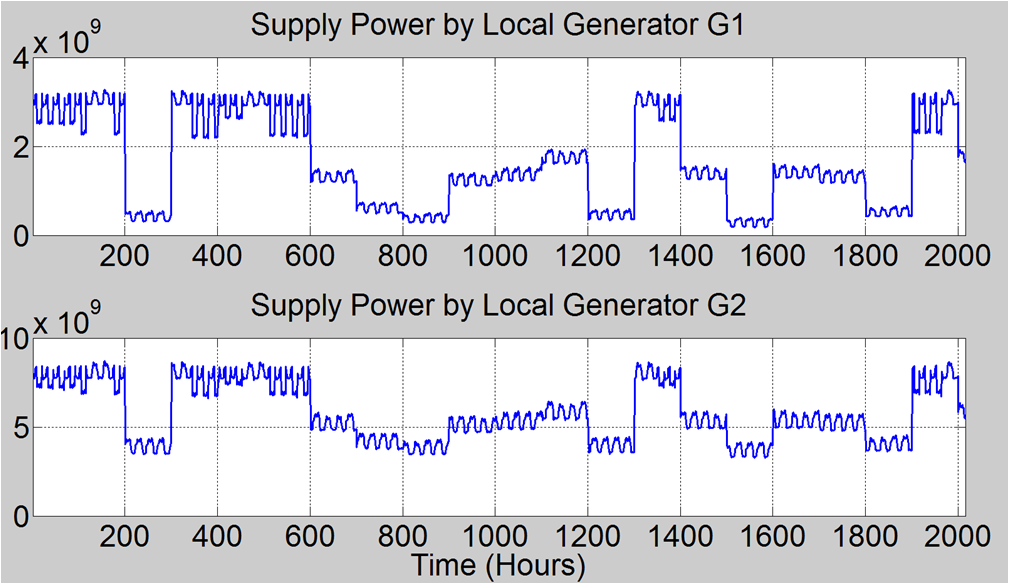 |
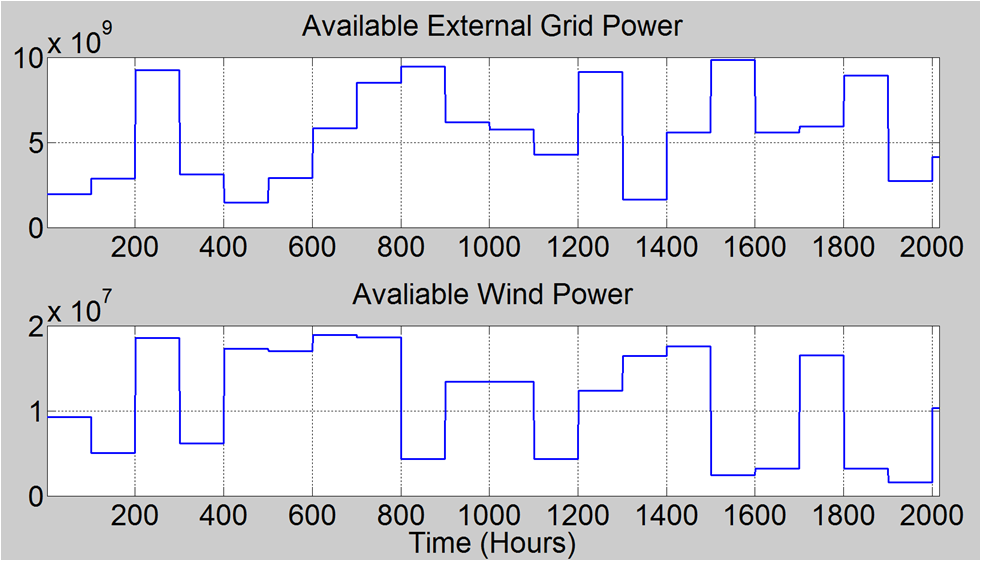 |
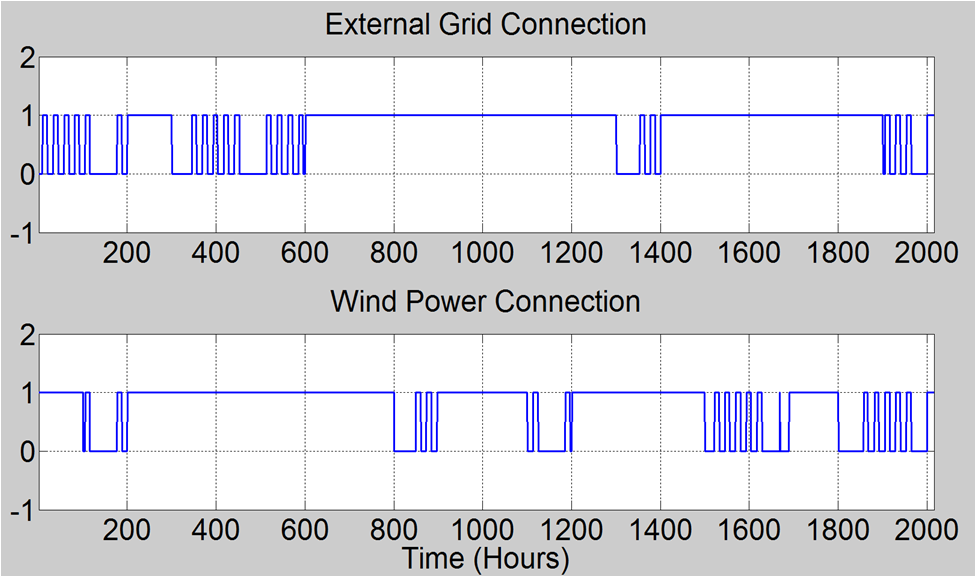 |