A Brief Look Into Economics
- Gross National Product (GNP) – is the total cash value of all goods and services sold on the open market over a given period, usually a year.
- GDP – Gross Domestic Product is almost the same, however, it differs by
- Subtract out Foreign Companies that make money in the US
- Adds US citizens making money in foreign countries
- Goods and Services (G and S) are calculated when a product is finally made
- What does "finally made" mean?
- Assume you want to build a car - start with the basics
- What do you need?
- Concept - "value adding" till the final product is made
- Value adding
- Car vs. its parts and labor that went into making ALL the parts - from fabric that went into a car to the final product
- If you counted both, the you would be counting the product x2
- Service
- Medical care, lawyer fees, waiters, anyone, that delivers a service to our economy
- Over the years we have transitioned from an industrial economy to a service economy
- What category does health care professionals fall into?
- GNP and GDP
... A short video on GNP and GDP
- Expenditure approach – is the sum that estimates all monies spent on G and S by households (consumption), business (investments), government (what they buy), and what people use outside our country that have purchased US goods (exports)
- Income approach – Estimates earned income that includes: wages, salaries, profits, rental income, and interest income (on the plus side). On the negative is depreciation that removes money from this calculation
- Output or product approach – sum of all output from any person or organization that produces G and S. Cost for raw materials and depreciation is subtracted from this amount.
- GNP does not
- Accounts for inflation
- Does’t look at home repair done by the homemaker
- Not applied - housekeeping, stay at home moms, donations, etc.
- No assessed - black market or under-the-counter transaction
- Issues about GNP
- If you have a natural disaster, the cost to clean it up reflects as positive expenditure towards the GNP
- According to some statistics while GNP has increased over the last 30 years, if you apply inflation to individual salaries the net effect is a negative loss
- How does inflation effect you annual income? Calculate
- GNP does’t think green. The more you buy and spend to replace objects you already own the more GNP improves
- If you want know more about the GNP http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gross_national_product

- GDP
- The difference between GNP and GDP is the income from foreign sources
- GDP will be ~ 21,990 Billion dollars in 2020
- If you subtract out depreciation from GDP or GNP you generate (Net) NNP or NDP. More information on National and Domestic Products:
http://www.cftech.com/BrainBank/FINANCE/GDP.html
- What do you think of these numbers? US import 3.1 trillion dollars and exported 2.5 trillion dollars in 2019
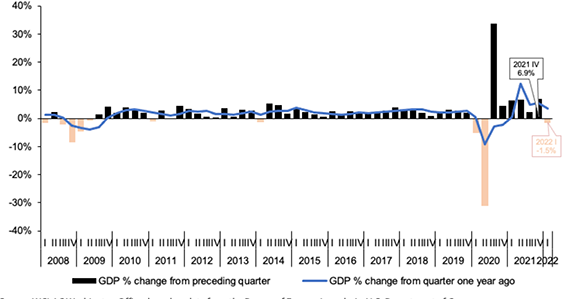
- A look at the GDP over time. Can you explain why it went into negative dollars?
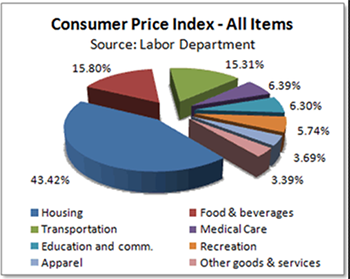
- Consumer Price Index (CPI)
- This is the average price of consumer goods and services purchased by households in the GDP
- It looks at a specific group of goods that hypothetically reflect your typical market price
- If the cost of the these specific goods go up, then an increase in inflation
- Likewise, if CPI prices go down then inflation drops
- Comments on Personal Income from an economic point of view
- Gross Income - Income Taxes = Disposable Income
- Disposable income - necessities = discretionary (spend or save)
- Inflation
- How has inflation affected us?
- What are the main causes of inflation?
- When demand goes up for product or service
- Cost to make the product goes up
- Increase in money supply
- Rising wages
- Monetary and fiscal policies
- Tacking the Consumer Price Index (CPI) which is composed of goods and services. This includes: food and berverages, housing, apparel, transportation, medical care, recreation, eduction, and communication.
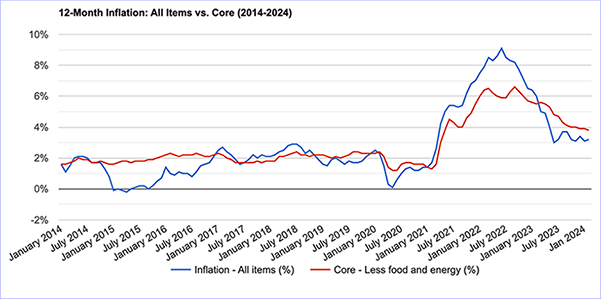
- Inflation from 2014 to 2024. Note how most of it stayed within a 2% range. However, COVD changed all that!
- Let's calculate - link
Elasticity of Demand
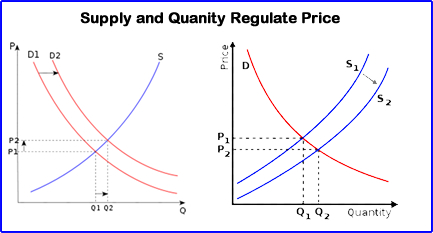
- It is important to see how a product will varies in price, which is based on its supply - quantity
- If supply goes up and demand stays the same, what happens to price?
- If demand goes up and supplies stays the same what happens to price?
- When a product behaves in this fashion, its demand is considered elastic
- Elastic vs. Inelastic
- Demand is elastic if price is influenced by supply and quantity
- Demand is inelastic when price is not influenced by supply and quantity
- Elasticity may also vary, in that a product can be only partially influence by demand and quantity
- Other factors, influence a products "relative in/elasticity"
- Percentage of a person's income
- Necessity for the product
- Duration - usually the longer a product will last the more elastic it becomes
- Substitutions
- Breath of definition - comparing other similar products. Example - Android vs Apple
Two schools of Classical Economics
- Classical Economics
- Is the heart of capitalism
- Supply and Demand
- Technology
- Investments
- Let business grow, with little to no governmental influence
- Keynesian - economy must be stimulated!
- In times of economic down turn interest rates need to be reduced
- Government needs to invest in infrastructure
There is so much more to say, but for that you need to enroll in a business course or two
Return to the Table of Content
4/24




