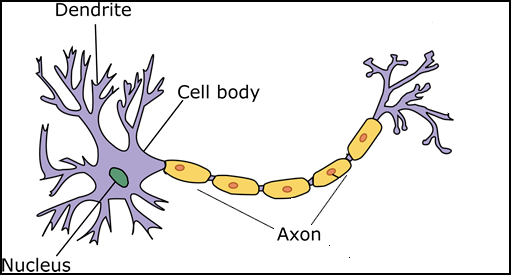
- Neurons
- Parts of
- Cell body - contains the nucleus that regulates the cell via its genetic materials
- Dendrites - branch out to other neurons sending and receiving information
- Axon - transmits the messages
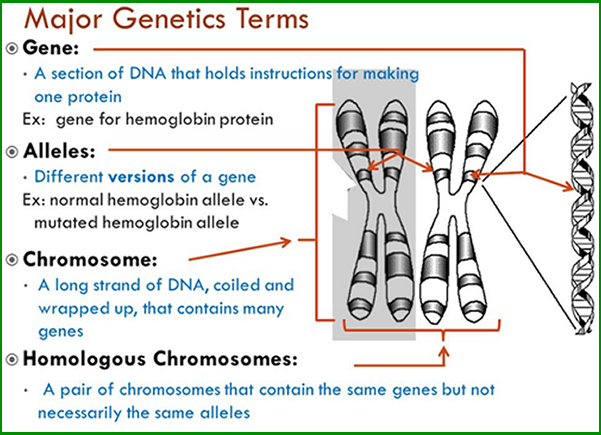
- Parts of
- Chromosomes, Alleles, and genes defined
- Pathology of disease
- It appears to be a gene problem, however, the exact genetic causes has not been identified. Other associated risk factors appear with variations chromosome 19 on the allele apolipoprotein E gene (APOE)
- APOE ε2 - rare and may prevent early onset on disease
- APOE ε3 - doesn't appear to either increase or decrease the probability of disease
- APOE ε4 - risk increases and usually appears early. However, some people that have this anomaly may never get AD, while other that don't have this allele get AD
- Other risk
- Mutations with chromosomes: 1, 14, and 21
- Presenilin 1 (gene) on chromosome 14 creates abnormal proteins
- Presenilin 2 (gene) on chromosome 1 creates abnormal proteins
- These create amyloid plaque
- Early onset occurs between 30 to mid 60s at less than 10% of the AD population
- If a mother or father has early onset, the child has ~50%
- Many other factors may also contribute, such as: stroke, high blood pressure, diet, mental stimulation, etc..
- Again the exact cause is still under investigation
- Mutations with chromosomes: 1, 14, and 21
- These genes generate protein for cell construction, operation, and repair. It appears that these abnormal genes generate proteins that may cause AD. As an example
- Chromosome 21 forms abnormal amyloid precursor protein (APP) and/or
- Chromosome 14 creates a mutation of presenilin 1
- Chromosome 1 creates a mutation of presenilin 2
- These mutations breakdown APP, but in an abnormal way, by generating amyloid plaque
- Neurofibrillary tangles
- Generated from tau, which is an abnormal protein that is formed by hyperphosphorylation
- Normally microtubles are formed within the nerve cell which transports information within the cell
- These abnormal tangles cause the microtubles to collapse
- Tau formation is normal unless hyperphosphorylation occurs
- There are other diseases associated with hyperphosphorylation of microtubles

- It appears to be a gene problem, however, the exact genetic causes has not been identified. Other associated risk factors appear with variations chromosome 19 on the allele apolipoprotein E gene (APOE)
http://slideplayer.com/slide/9742228/ (not active)
- There are three different agents approved for imaging AD

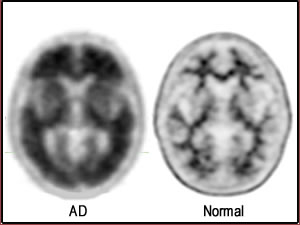
https://basicmedicalkey.com/dementia-and-its-treatment/- First you may recall what AD looks like when imaging with FDG
- Atrophy causes reduced uptake of the radio tracer
- Initially effecting the parietal and temporal lobes in a bilateral fashion
- As AD progress reduced uptake occurs in the frontal areas of the brain
- It is important that you understand the difference between Amyvid and FDG!
- 18F-florbetapir (Amyvid from Eli Lilly) The greater the plaque the greater the uptake
- Is a peptide that has an affinity for β-Amyloid plaque
- The greater the plaque the greater the uptake
- Dose is 10 mCi, delayed images start 20 to 50 minuts post dose, acquire data for 10 minutes on a single bed
- 18F-flutemetamol (Vizamyl from GE Healthcare)
- This is a thioflavin derivative ot "Pittsburg compound B (PiB)
- Will specificially attach to β-Amyloid plaque
- 5 mCi dose, delayed image starts 45 to 180 minutes post dose, acquire a single bed position for 15 to 20 minutes
- 18F-florbetaben (NeuraCeq from Piramal Pharma)
- This agent was 100 sensitive and 92% specific in detecting AD
- Is a stilbene derivative
- Has an affinity β-Amyloid plaque
- 8 mCi dose, delayed images start 90 post dose, acquire single bed position for 20 minutes
https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/762347
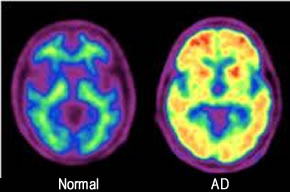
- First you may recall what AD looks like when imaging with FDG
