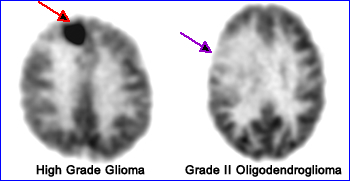

Case I - Variations in FDG uptake and the role of target of background1
High grade Gioblastomas usually have significant uptake, however, it some cases a high grade tumor might have activity similar to gray matter. Whereas low grade glioma's have less uptake, generally are less aggressive, and may have activity that matches or is less than white matter. The above example shows a high grade tumor greater than gray matter and a low grade tumor is that has less than white matter. Note - Gray matter to white matter ratio = 2.5 to 1
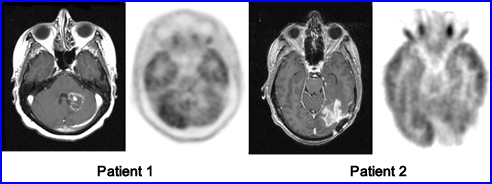
Case II - Evaluation of stereotactic radiosurgery on different types of brain tumors1
Patient 1 had metastatic breast cancer in the brain. Following surgery there is a lack of FDG uptake around the are of the tumor sight. MRI scan only shows necrosis at the site of the tumor. Conclusion - Tumor regression had occurred
Patient 2 had radiosurgery of a glioblastoma. Follow-up MRI was positive and FDG study indicates increased tracer uptake along the edges of the surgical site
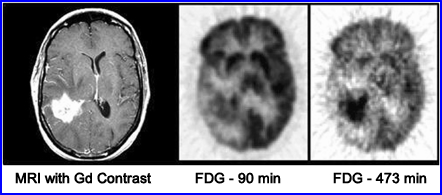
Case III - Extending the time between injection and scanning1
Enhanced MRI shows a right temporal glioblastoma, however, the 90 minute delayed FDG scan shows only moderate uptake at the tumor site. A second delay scan was completed which showed significantly uptake of the tumor
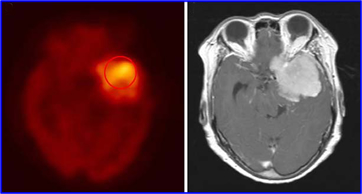
Case IV - Grade I Meningioma2
Meningiomas are benign intracranial tumors that require removal. The main problem with this tumor is that it has a high rate of reoccurrence (grade 1 = 7%, grade II = 35%, and grade III - 73%). FDG can be used to evaluate tumor viability and FDG uptake depends on: tumor grade and its aggressive behavior. The above is an example of FDG uptake in a grade I meningioma
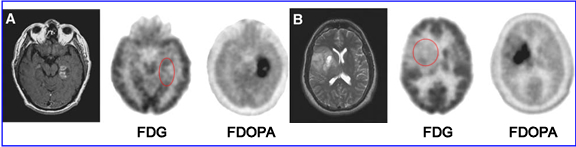
Case V - FDG vs. FDOPA3
Chen W et al. demonstrated that 18FDOPA does a better job in finding glioblastomas whether the tumor is high or of low grade and does a better job it when compared with 18FDG. The reason seems to be that FDOPA, as an amino acid analog, has higher target to background ratios (viable tumor to normal brain tissue). The images above demonstrate this fact
1 - Clinical Applications of PET in Brain Tumors* (2007)
2 - 18F-FDG PET in the assessment of tumor grade and prediction of tumor recurrence in intracranial meningioma. Lee, JW, et al. (2009)
3 - 18F-FDOPA PET imaging of brain tumors: comparison study with 18F-FDG PET and evaluation of diagnostic accuracy. Chen W, et al. (2006)