- The BBB controls the movement of substances to and from the vascular pool and the brain's extracellular fluid (CSF)
- Allows specific nutrients required by the Brain to pass to and from the cells within the brain
- Protects the brain from toxic chemicals
- Capillaries in the brain have tight endothelial junctions and a continuous basement membrane - prevents large molecules from being absorbed by the neurons
- Astrocyte foot processes are the other component of the basement membrane and it restrict entry of certain materials at the cellular level
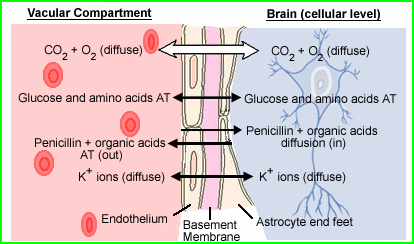
Image was modified http://137.222.110.150/calnet/Blood/page2.htm
- Radiopharmaceuticals for the brain can be classified into two different categories: those that do not cross the blood brain barrier (BBB) and those that do cross the BBB
- Those that do not cross the BBB
- 99mTc pertechnetate (04-) with NaClO4- or KClO4- (200mg 1.5 to 8 hours prior to injection)
- 99mTc diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid (DTPA)
- 99mTc glucoheptonate (GH)
- Those that do cross the BBB
- 99mTc d, 1-hexamethylpropyleneamine (HMPAO)
- 99mTc N, N'-1,2-ethylenedyiylbis-L-cysteine diethylester (ECD)
- Here are some other examples of brain imaging agents that will not be covered this semester (these cross the BBB)
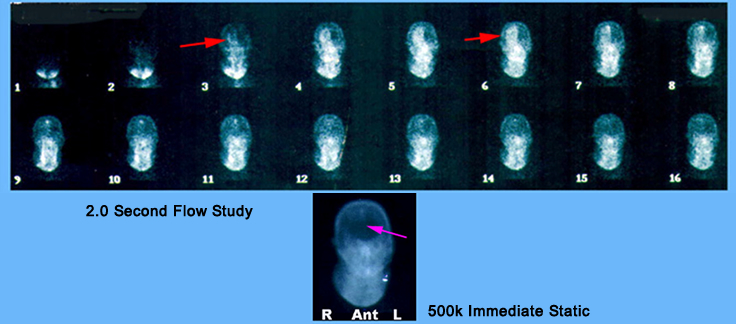
- Radiopharmaceuticals that do not cross the BBB contain 3 different imaging components during the procedure: dynamic, immediate static, and delays
- Part I - Dynamic
- Administer IV 20 to 30 mCi
- Place the patient's neck and head within the camera's FOV
- This can be done either ANT or POST (consider the pathology of interest)
- Set the flow study to 2-second per frame and inject, IV bolus: 99mTc DTPA or GH or 99mTc04-
- Dynamic images are then collected for one to two minutes
- Part II - Immediate Static
- Complete an immediate static image ~500k in the same position
- If there is any abnormal pooling, consider taking additional static images around the area of interest
- Part III - Delayed images
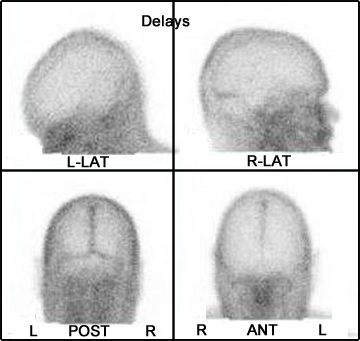
- The above images are an example of a normal brain scan with the sinuses labeled
- If pertechnetate is used, delayed imaging should be done no less than 2 hours post IV injection
- If GH or DTPA is used imaging may start at 1.5 hours (related to increased excretion of the radiopharmaceutical)
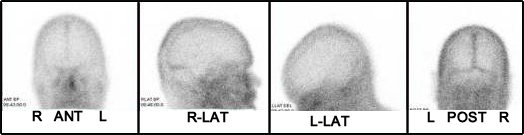
- When imaging the brain, exclude as much of the facial activity as possible (extensive, non-essential activity is seen below the obits of the eyes)
- Take 500k images of ANT, POST, R-LAT, and L-LAT
- A vertex view is required when abnormalities are noted around the upper portion of the brain (superior sagittal sinus)
- If suspicious/questionable (increased) activity is seen anywhere in the brain, further delay imaging is warranted (one to two hours later)
- The Physiology behind these types of radiopharmaceuticals
- Lack of blood flow to the BBB will result in the lack of uptake in brain - brain death
- Delayed blood flow on the affected side is an indication of stroke - may be referred to as the flip-flop phenomenon
- Increased blood flow in the dynamic phase indicates a highly vascularized area - vascular tumor or AV malformation
- On delayed images increased uptake in the brain occurs when there is damage to the BBB (examples are stroke and tumor)
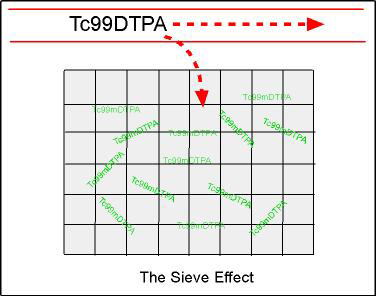
- Sieve effect - As the diagram indicates, when an area is damaged (gray area), the radiopharmaceutical becomes trapped; as trapping increases, uptake in the area can be seen
- In addition, the radiopharmaceutical is quickly excreted out of the blood via the kidneys, reducing background levels in the vascular pool and giving better target to background allowing for better visualization of the damaged area of the brain
- Dynamic and immediate pooling are displayed with no abnormalities
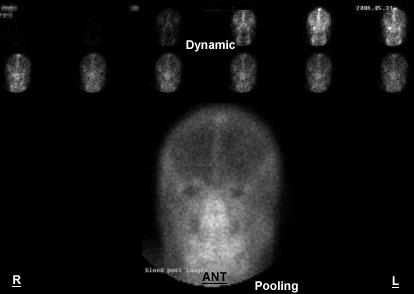
http://surge.ods.org/xeleris/xeleris.htm - Normal
- Activity ascends up the left and right common carotids and the vertebral arteries. The arterial flow shows bilateral symmetry through its arterial and venous phases. When the superior sagittal sinus "lights up" (top/center of the head) flow enters its venous phase
- The 1.5 hour delays continue to show normal tracer distribution
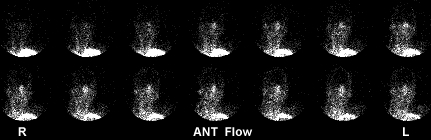
- Brain death
- Only needs a flow study to be confirmed, however, immediate statics are usually acquired
- Lack of blood flow to the brain indicates brain death
- This is caused by swelling around the base of the brain, which cuts off blood flow
- Further indication is the lack of sinus activity (venous phase) means no venous return
- Do to advances in radiopharmaceutical development this might be the only real use of these radiopharmaceuticals. However, they can technically be used to diagnose: stroke, brain mets, abscess, and primary brain cancer
- The above patient was sent to nuclear medicine for brain death evaluation. History indicated that the patient had shot himself in the head. What do the results of the exam indicate?
- Is there blood flow?
- Where is the blood flow? [Hint] Red arrow is the area of a penetrating bullet
- Do you see any sinuses [Hint] Purple arrow is the area of the sagittal sinus
- Do you see the superior sagittal sinus?
http://www.miracosta.cc.ca.us/home/lmoon/death.html
- 99mTc-hexamethyl propylene amine oxime (HMPAO)
- At first pass 72% is as it crosses the BBB
- This initially lipophilic compound becomes hydrophilic after it attaches to a neuron
- Part of the agent will diffuse back into the bloodstream
- It reaches equilibrium within 2 minutes and stays constant for 8 hours
- Methylene blue creates a stabilizes product for four hours
- Has a slower washout rate when compared to ECD
- 99mTc -ethyl cysteinate dimmer (ECD)
- Similar to HMPAO
- Lipophilic becomes lipophobic when it attaches to a neuron
- Expiration time is six hours
- As for an advantage over HMPAO - imaging can be done sooner and target to background is better
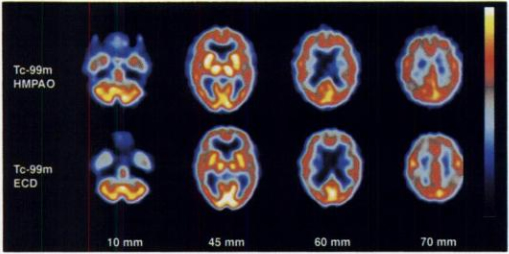
http://jnm.snmjournals.org/content/37/11/1749.full.pdf+html?sid=36254f59-88cd-4513-8772-485d5c503b4b - Comparing ECD and HMPAO in a patient that has possible Alzheimer's disease
- ECD appears to have greater "contrast" (color scale variation)
- Look at the 60 min and 70 min in the area the parietal area of the cortex
- More variation is seen with the uptake of the radiopharmaceutical
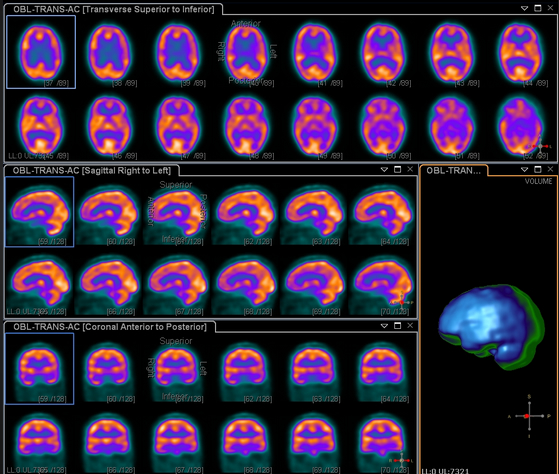
- The above are the images normally taken on a brain SPECT procedure
- Coronal, sagittal, and transverse
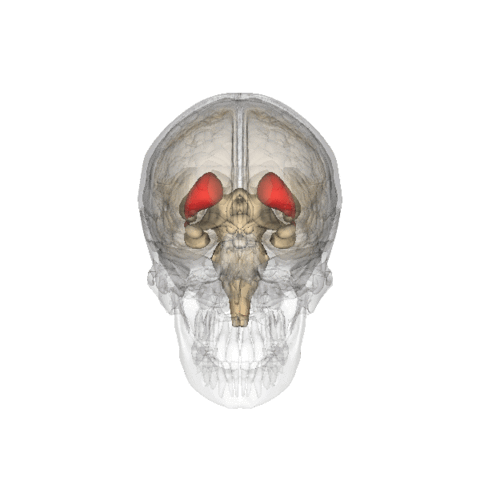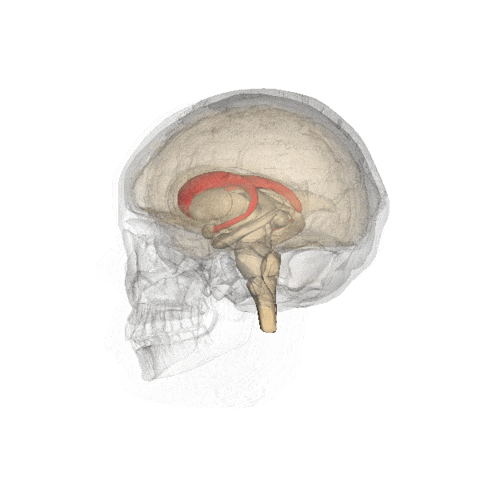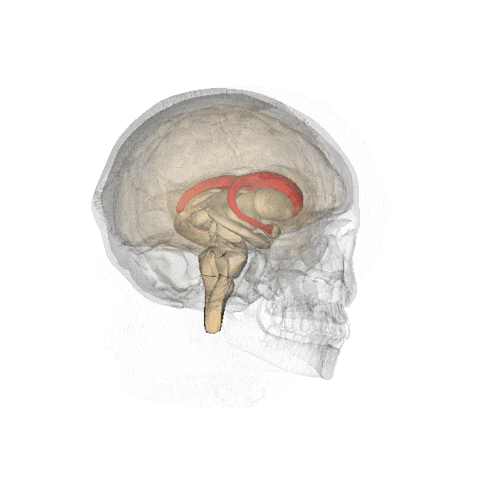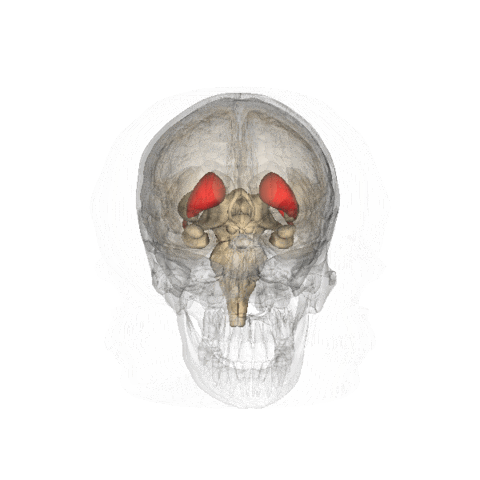
- DaTscan (123Ioflupane)
- It all has to do with dopamine production
- The organs of interest are the caudate nucleus (A) and the putamen (B)
- The lack of dopamine production at the pre-synaptic site causes a reduction of Ioflupane uptake within these structures
- Examples of normal and abnormal dopamine production in the brain
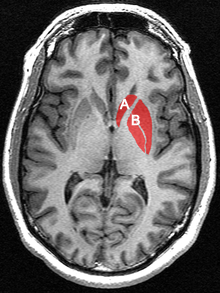
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Caudate_nucleus
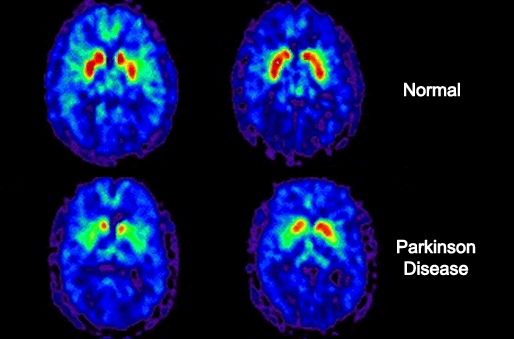
http://alfa-img.com/show/nuclear-medicine-brain-scan.html - PET imaging
- Here is a very brief view of the different radiopharmaceuticals used where PET imaging is applied
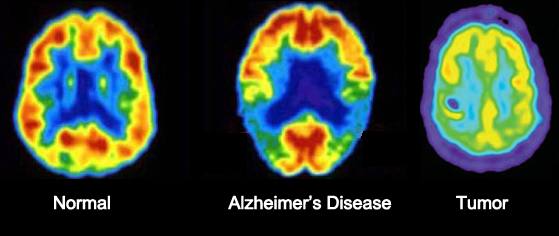
- FDG - the brain works mainly on sugar for its energy. FDG is a fake sugar so it freely passes the BBB and becomes trapped in the glycolysis process within brain tissue
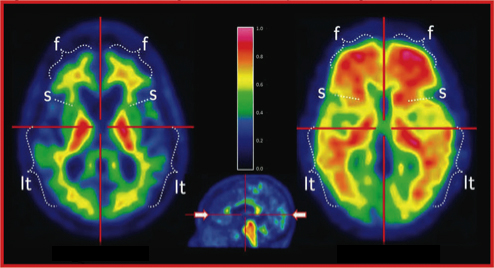
- Transverse slice on the far right shows normal brain uptake
- The image shows loss of activity in the temporal and parietal lobes. Advanced disease shows lose of activity in the frontal lobe
- Far left shows a glioblastoma. Cold in the center where there is loss of blood flow and activity. However, in the otter rim activity increases, which indicates active tumor
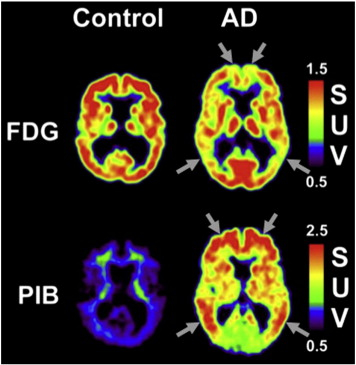
- Another area in PET brain is a more specific method to imaging Alzheimer's Disease
- Vizamyl and other related radiopharmaceuticals will specifically bind to amyloid plaque or Tau tangles
- The above left shows a normal pattern of uptake in the white matter. However, on the right amyloid plaque has significantly invaded the gray matter which in turn causes increase tracer uptake
- Difference between amyloid plaque and FDG imaging
http://aticplaza.com/?page_id=21
Return to the beginning of the document
Return to the Table of Contents
A Clinical Manual of Nuclear Medicine, by JM Walker and D Malefactor. Appleton-Century-Crofts/Norwalk, CN 1984