Schillings I, II, and III Procedures
Schillings Formula
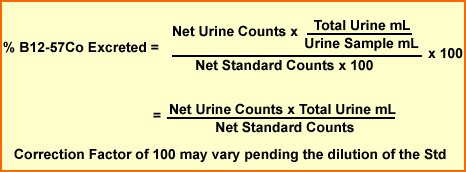
Schillings I
- Give PO 57Co(Cyanocobalamin) capsule - approximately 0.1μCi
- One to two hours post dose administer 1000U stable B12 IM
- Have the patient collect a 24 hour urine
- When the 24 hour urine arrives refrigerate it for several hours to reduce the temperature and smell
- Measure the volume
- Pipette 4 mL of urine and place into a test tube for counting
- Count the urine for at least 15 minutes and as much as 30 minutes - remember your counting statistics!
- Count the background for the same amount of time as the sample
- Apply your data to the above information
- Normal vs. Abnormal results
- Mallinckrodt package insert says, "0 to 3 percent is pernicious anemia or some other condition preventing absorption of the B12
- 3 to 5 percent is questionable
- Greater than 5% is normal
- Other literature indicates that normal is between 8 to 10 percent
Schillings II
- Is done when Schillings I is considered abnormal
- When administering the dose of 57Co-B12 also administer, PO intrinsic factor
- Continue with the application of steps 2 - 9
- If this is abnormal go to Schillings III
Schillings III
- Administer IV antibiotic therapy for 7 to 10 days
- This will destroy bacteria in the GI track that may be preventing the absorption of B12
- After therapy repeat Schillings one and include the administration of intrinsic factor
Comments
- Urine Collection must be done over a 24 hours period
- Why is 100(%) not used in the formula? 100 (%) and correction factor is 100.
- Make sure you know the difference between Schillings I, II, III
- Understand the Schilling's Procedure includes
- Reason for the injection of stable B12
- Application of intrinsic factor
- Use of IV antibiotics
Return to the Table of Content
12/14

