Diseases
- Aplastic anemia
- Disease shows failure within the bone marrow that produces red/white cells and platelets
- Usually there is an increase in yellow bone marrow that may invade the red bone marrow within the central skeleton
- While disease may be the cause (viral hepatitis), certain drugs or chemicals (benzene, choramphenicol, quinine, etc.) it has also been related to the lack of iron in the diet
- Lose of bone marrow uptake would be an indication of Aplastic anemia
- Pattern with Thrombocytopenia, myelocytic leukemia, and Polycythemia Vera
- Initially the central skeleton looks normal
- As disease progresses, there is failure within the central skeleton to produce the appropriate cell components that causes expansion of the red marrow into the axial skeleton and peripheral long bones
- Further progression of the disease will show increased splenic uptake when 52Fe is administered, however, there is no increase in spleen size
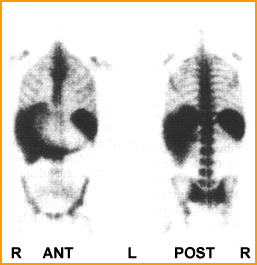
- The left image1 shows activity extending down into the the patient's knees as well as extensive spleen uptake. This is an example of chronic lymphocytic leukemia and the radiopharmaceutical used was 52Fe
- The image1 on the right is a classic example of Polycythemia Vera taken with 52Fe. In this case the activity extends down to the knees and shows reduced uptake in the central skeleton
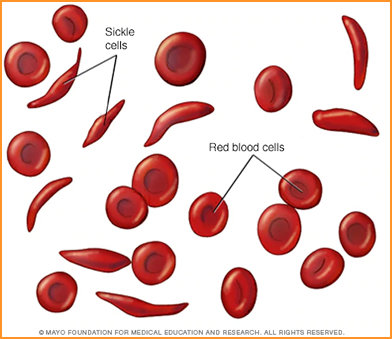
- Sickle cell anemia
- Genetically altered red blood cells can cause infarct and ischemia with bone tissue/marrow as well as other areas of the body
- In general, infarct/ischemia is not seen in the bone marrow, however, increased activity is noted in the axial skeleton and peripheral bones
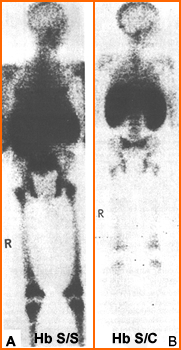
- Two types of sickle cell anemia1 are identified above
- Hb F is fetal hemoglobin that becomes Hb A (adult) and occurs in about 95% of the population
- Hb S/S is a form of sickle cell hemoglobin that shows extensive homogeneous activity in the peripheral and axial skeleton. In addition the liver and spleen may be enlarged
- Hb S/C is another variation of sickle cell that shows similar involvement (axial and peripheral bone) but with reduced uptake
- Whole Body Radiation Therapy
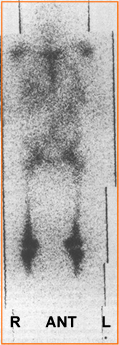
- This causes loss of bone marrow production, but over time bone marrow function returns. Usually activity in the hemopoietic system starts up within a several months after therapy and normal distribution should return within the year

- The above image1 is an example of a patient that received a total of 4000 rads. At least 6 months post therapy 52Fe shows the return of red marrow production with a marked increased to the splenic area. The literature was not clear as to why there was significant spleen activity
Return to the beginning of the Document
Return to the Table of Content
1 - Images acquired from Diagnostic Nuclear Medicine, 3rd Edition, MP Sandler, et. al., vol 2, Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, 1996
2 - Comparative study of 111In and 59Fe bone marrow scanning by Parmentier, C, et al., European Journal of Nuclear Medicine
3 - A comparison of 111In with 52Fe and 99mTc-sulfur colloid for bone marrow imaging by Merrick, MV, et al., JNM
4 - Bone-Marrow Imaging with Indium-111 Chloride in Aplastic Anemia and Myelofibrosis: Concise Communication by Sayle, BA, et al. JNMT
5 - >Differences in Distribution of Erythropoietic and Reticulendothelial Marrow in Hematologic Disease by Dyke DV, et al Blood
9/23