Amyloidosis with a focus on Cardiac
- What is Amyloidosis?
- The types of disease
- Are disease is a build up of protein (amyloid)
- This can occur in many different areas of the body - heart, liver, spleen, CNS, kidneys, or GI
- Types of Amyloidosis
- AL Amyloidosis (primary) - plasma cell disorder that comes from monoclonal immunoglobulin light chain. These fibrils can occur anywhere in the body
- AA Amyloidosis (secondary) - comes from infections and inflammation that generates the amyloid fibrils. Usually begins in the kidneys.
- ATTR (m or wt) Amyloidosis -
- ATTRm is an inherit mutation of transthyretin (TTR) protein that generates fibrils that cause cardiomyopathy or neuropathy that usually occur in people over 40
- There are more than 100 types of TTR
- ATTRwt is considered an non-mutated protein that may cause cardiomyopathy in older men
- There are other types of Amyloidosis which includes: Apolipoproteint A-I (AApoAI), Apolipoprotein A-II, Gelsolin (AGel), Fibriogen (A Fib), Lysozyme (ALys), Beta-2 Immunoglobulin Amyloidosis (Abeta2m), and Localized Amyloidosis (ALoc)
- Our focus is with ARRT Amyloidosis that affects the function of the myocardium
- ATTR is our focus and it is most commonly found in men in their 70s and to a lesser extent in their 60s
- One in four men have some ATTR their 80s, but it does not appear to have any effect
- Deposits of ARRT occur in the LV that cause myocardial wall thickening
- ~4% of US African Americans acquire ARRTm that may contribute to heart failure
- Diagnosing AL
- Echocardiography or MRI has been used to diagnose this disease
- The application of 99mTc-PYP appears to be a viable alternative assess and manage these patients
- Nuclear Medicine Procedure
- No patient preparation is needed
- Administer 10 to 20 mCi of 99mTc-PYP IV
- Delayed images can occur at 1 and/or 3 hours post dose
- LEHR collimator
- Planar imaging use 256 matrix
- SPECT imaging use 128 matrix
- Planar images
- ANT, L-LAT, and LAO
- 750k counts
- MAG @ 1.46
- SPECT (assume this is a dual headed camera)
- 180 degree acquisition
- No gating
- Number of stops ~40
- Twenty seconds per stop
- MAG 1.0
- Assessment of myocardial uptake
- Grade Zero = No myocardial uptake uptake + normal rib uptake
- Grade One = Myocardial uptake less than ribs
- Grade Two = Myocardial uptake equal to ribs
- Grade Three = Myocardial uptake greater than ribs
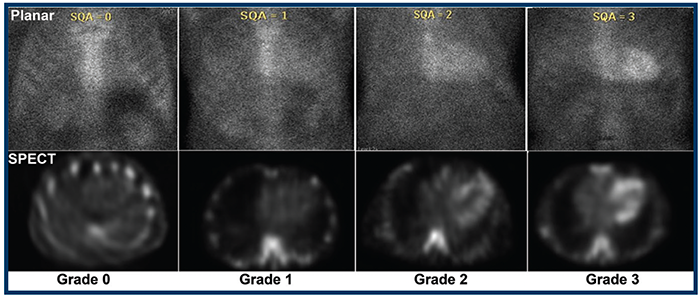
- Example of Grades 0 through 3
References
1. Types of Amyloidosis, Boston University, Amyloidosis Center. https://www.bu.edu/amyloid/what/types/
2. 99mTechnetium-Pyrophosphate Imaging for Transthyretin Cardiac Amyloidosis, ASNC - link
10/23
