Differential Equations Quiz #7 April 13, 2005
Name____________________ R. Hammack Score ______
_________________________________________________________________________________
(1) Find the general solution of the differential equation y' '- y = x
Looking at the associated homogeneous equation y''-y = 0,
you can see that its auxiliary equation is
It follows that the complementary function is
Now, the D.E. that we want to solve is (
so we apply the annihilator operator
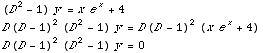
the roots are -1, 1, 1, 1, 0 so the general solution is
y =
with
Note
And
Or
Plugging
(2A + 2B)
(2A + 2B)
From this we see C = -4, B = 1/4, and A = -1/4.
SOLUTION: y =