Fluciclovine (Axumin) for Prostate Cancer Imaging
- Prostate cancer - biochemically recurring prostate cancer (BRC)
- Regulate amino acid transporter
- Glutamine transporters ASCT2 and LAT1 are the most prevalent
- Transporters are found in larger quantities on the surface of prostate tumor cells
- Thse transporters assist in the spread of disease
- Axumin is a PET 18F radiopharmaceutical used to diagnose, stage, re-stage prostate cancer. A four minute video is available at https://www.axumin.com/about/moa
- Mechanism of uptake
- Tracer is a synthetic amino acid that mimics glutamine
- Transported into the cancer cells
- Since it is not incorporated into the cancer cells, over time, it washes out of the cell
- Uptake
- Occurs in the prostate bed, lymph nodes, and bone
- It identifies all prostate cancers 77% and 90% are found outside the prostate bed
- Uptake appears to be related to PSA levels
- Teyateeti A, et al - In a small study of patients with undetectable PSA levels
- 4 of 324 were positive
- Positive had a Gleason score of 7 or higher
- Staging was T3-T4
- Scarsbrook AF - Studied the management of biochemical recurrence (BCR) in 104 patients
- Disease was detected in 58 of 104
- Only 1 of three patients were positive with a PSA value of < 1.0 ng/mL
- 93% were positive if PSA value was > 2.0 ng/mL
- Calsis J -68Ga-PSMA-11 vs 18F-Fluciclovine - future direction?
- In a small study of 10 patients
- These two radiotracers were compared and the results indicated that PSMA tracer
- Further evaluation needs to be initiated
- Procedure guideline for prostate cancer imaging (version 1.0)
- Indications
- Assessing BCR appears to indicate that any PSA above >0.2 ng/mL requires further assessment and possible therapy
- Sensitivity of Axumin increases with higher Gleason score levels
- Cancer within the prostate bed has a high sensitivity and low specificity
- Outside the prostate bed there is a high to mid sensitivity (55%) and high specificity (97%)
- Regional distal mets varied based on PSA levels in a study of almost 600 patients
- 0.8 to 2.03 ng/mL sensitivity ~60% (21 - 39% distal)
- 2.04 to 6 ng/mL sensitivity ~75% (45% distal)
- >6 ng/mL 85% (60% distal)
- High correlation to metastatic bone, however, a bone scan should be done even when Axumin is negative
- Axumin has a major effect in altering radiation therapy to the prostate bed (reducing it). Why?
- Uptake
- Raped uptake occurs in cancer cells - peak tumor to surrounding tissue occurs 4 to 10 minutes post injection and plateaus at 30 minutes
- Washout begins at 15 minutes with 61% reduction at 90 minutes
- Lymph node avidity has rapid uptake and a faster washout when compared to prostate cancer
- Imaging protocol and processing
- Patient should be on the imaging table when receiving a bolus injection of the tracer
- Injection is preferred in the right arm which should be elevated after the injection is complete
- Start transmission scan
- At 3 - 5 minutes post inject the PET acquisition should begin
- Zero to five minute dynamics can be taken over the prostate bed
- Body scan should start at the base of prostate bed to include inguinal lymph nodes to the base of the skull
- If lower extremities are required then complete this as the second part of the imaging procedure
- If scanning is delayed for up to 30 minutes then imaging time per bed should also be increased
- CT with contrast does not appear to help in the diagnosis
- TOF is recommended
- Reconstruction with a point sped function (PSF) is recommended
- CT bone window is recommended
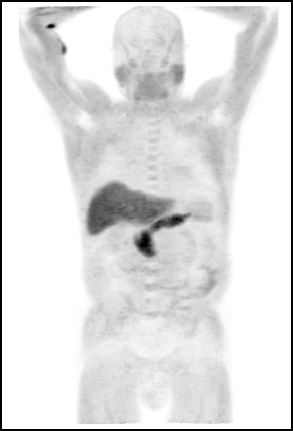
- Normal distribution of Axumin with no disease present - tissue uptake occurs in pancreas and liver (greatest intensity), salivary and pituitary (moderate), muscle and bone marrow (moderate to mild)
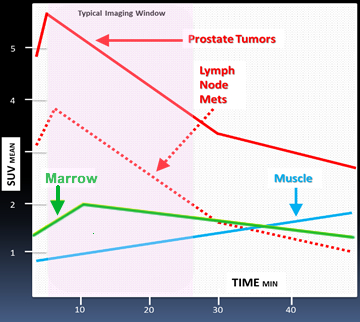
- Biodistribution of Axumin in normal and abnormal tissue
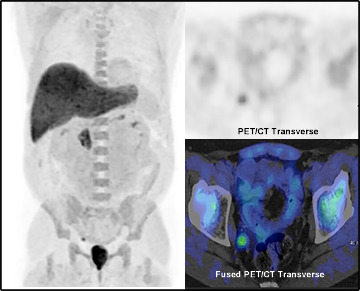
- Positive Axumin with lymph node involvement
- False positive findings include - benign prostatic hyperplasia, post-radiation inflammation, and fibrosis. Ringworm, and musculoskeletal or skin
Reference
3/21


