
|
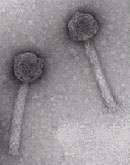
Comparative genomics of P2-related phages P2 is a temperate phage that belongs to the family Myoviridae. P2-like phages are widespread among the gamma proteobacteria. Complete genomes of a number of P2-related phages are now available, and a number of related prophages are found in sequenced bacterial genomes. Comparison of these genome sequences supports a model for modular phage evolution. P2-related phages and cryptic prophages encode a variety of lysogenic conversion functions. Some of these, like the sopE gene encoded by a P2-related prophage in Salmonella enterica, have been implicated in bacterial virulence. Others, like the nucC gene encoded by a cryptic prophage in Serratia marcescens, have been adapted for the regulation of genes in the bacterial host. The tum module, present in a subset of these phages, allows UV-induction of the prophage. We are characterizing lysogenic conversion genes encoded by a several P2-related phages in order to elucidate the horizontal transfer of these genes and to understand the contributions of these genes to the physiology of the bacterial host. |





